The Mechanism of Action and Clinical Efficacy of Low-Dose Long-Term Macrolide Therapy in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
- PMID: 37298439
- PMCID: PMC10253369
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119489
The Mechanism of Action and Clinical Efficacy of Low-Dose Long-Term Macrolide Therapy in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Abstract
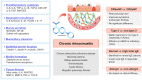
Various chronic inflammatory airway diseases can be treated with low-dose, long-term (LDLT) macrolide therapy. LDLT macrolides can be one of the therapeutic options for chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) due to their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory actions. Currently, various immunomodulatory mechanisms of the LDLT macrolide treatment have been reported, as well as their antimicrobial properties. Several mechanisms have already been identified in CRS, including reduced cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-8, IL-6, IL-1β, tumor necrosis factor-α, transforming growth factor-β, inhibition of neutrophil recruitment, decreased mucus secretion, and increased mucociliary transport. Although some evidence of effectiveness for CRS has been published, the efficacy of this therapy has been inconsistent across clinical studies. LDLT macrolides are generally believed to act on the non-type 2 inflammatory endotype of CRS. However, the effectiveness of LDLT macrolide treatment in CRS is still controversial. Here, we reviewed the immunological mechanisms related to CRS in LDLT macrolide therapy and the treatment effects according to the clinical situation of CRS.
Keywords: chronic rhinosinusitis; cytokines; macrolide; nasal polyps; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Past, present and future of macrolide therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016 Apr;43(2):131-6. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.08.014. Epub 2015 Oct 4. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2016. PMID: 26441370 Review.
-
The role of macrolides in chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025 Feb 1;25(1):19-26. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000001050. Epub 2024 Nov 25. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39584537 Review.
-
The Role of Macrolides in Chronic Rhinosinusitis (CRSsNP and CRSwNP).Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017 May;17(5):30. doi: 10.1007/s11882-017-0696-z. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2017. PMID: 28429305 Review.
-
The Role of Macrolides and Doxycycline in Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2020 May;40(2):303-315. doi: 10.1016/j.iac.2019.12.005. Epub 2020 Jan 18. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 32278453 Review.
-
Macrolide therapy of chronic rhinosinusitis.Rhinology. 2007 Dec;45(4):259-67. Rhinology. 2007. PMID: 18085018 Review.
Cited by
-
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024 Sep 20;121(19):643-653. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2024.0167. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2024. PMID: 39173076 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kudoh S., Azuma A., Yamamoto M., Izumi T., Ando M. Improvement of survival in patients with diffuse panbronchiolitis treated with low-dose erythromycin. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998;157:1829–1832. - PubMed
-
- Kricker J.A., Page C.P., Gardarsson F.R., Baldursson O., Gudjonsson T., Parnham M.J. Nonantimicrobial Actions of Macrolides: Overview and Perspectives for Future Development. Pharmacol. Rev. 2021;73:233–262. - PubMed
-
- Culić O., Eraković V., Parnham M.J. Anti-inflammatory effects of macrolide antibiotics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001;429:209–229. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical