Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and Its Interplay with Inflammation
- PMID: 37298632
- PMCID: PMC10254034
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24119677
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and Its Interplay with Inflammation
Abstract
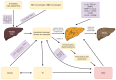
The prevalence of metabolic-related disorders, such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2), has been increasing. Therefore, developing improved methods for the prevention, treatment, and detection of these two conditions is also necessary. In this study, our primary focus was on examining the role of chronic inflammation as a potential link in the pathogenesis of these diseases and their interconnections. A comprehensive search of the PubMed database using keywords such as "non-alcoholic fatty liver disease", "type 2 diabetes mellitus", "chronic inflammation", "pathogenesis", and "progression" yielded 177 relevant papers for our analysis. The findings of our study revealed intricate relationships between the pathogenesis of NAFLD and DM2, emphasizing the crucial role of inflammatory processes. These connections involve various molecular functions, including altered signaling pathways, patterns of gene methylation, the expression of related peptides, and up- and downregulation of several genes. Our study is a foundational platform for future research into the intricate relationship between NAFLD and DM2, allowing for a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and the potential for introducing new treatment standards.
Keywords: chronic inflammation; cytokines; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; oxidative stress; pathogenesis; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Calabrese F.M., Disciglio V., Franco I., Sorino P., Bonfiglio C., Bianco A., Campanella A., Lippolis T., Pesole P.L., Polignano M., et al. A Low Glycemic Index Mediterranean Diet Combined with Aerobic Physical Activity Rearranges the Gut Microbiota Signature in NAFLD Patients. Nutrients. 2022;14:1773. doi: 10.3390/nu14091773. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Riazi K., Azhari H., Charette J.H., Underwood F.E., King J.A., Afshar E.E., Swain M.G., Congly S.E., Kaplan G.G., Shaheen A.-A. The Prevalence and Incidence of NAFLD Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022;7:851–861. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00165-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Loomba R., Morgan E., Watts L., Xia S., Hannan L.A., Geary R.S., Baker B.F., Bhanot S. Novel Antisense Inhibition of Diacylglycerol O-Acyltransferase 2 for Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multicentre, Double-Blind, Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020;5:829–838. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30186-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kedarisetty C.K., Bhardwaj A., Kumar G., Rastogi A., Bihari C., Kumar M., Sarin S.K. Efficacy of Combining Pentoxiphylline and Vitamin E versus Vitamin E Alone in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis—A Randomized Pilot Study. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2021;40:41–49. doi: 10.1007/s12664-020-01131-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

