Isolation, Identification and Molecular Mechanism Analysis of the Nematicidal Compound Spectinabilin from Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. DT10
- PMID: 37298840
- PMCID: PMC10254515
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28114365
Isolation, Identification and Molecular Mechanism Analysis of the Nematicidal Compound Spectinabilin from Newly Isolated Streptomyces sp. DT10
Abstract
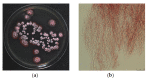
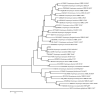
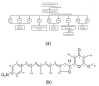
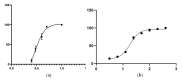
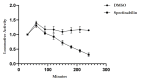
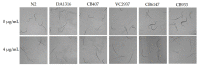
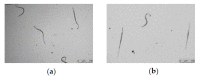
Plant parasitic nematodes (PPNs) are highly destructive and difficult to control, while conventional chemical nematicides are highly toxic and cause serious environmental pollution. Additionally, resistance to existing pesticides is becoming increasingly common. Biological control is the most promising method for the controlling of PPNs. Therefore, the screening of nematicidal microbial resources and the identification of natural products are of great significance and urgency for the environmentally friendly control of PPNs. In this study, the DT10 strain was isolated from wild moss samples and identified as Streptomyces sp. by morphological and molecular analysis. Using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model, the extract of DT10 was screened for nematicidal activity, which elicited 100% lethality. The active compound was isolated from the extracts of strain DT10 using silica gel column chromatography and semipreparative high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The compound was identified as spectinabilin (chemical formula C28H31O6N) using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Spectinabilin exhibited a good nematicidal activity on C. elegans L1 worms, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 2.948 μg/mL at 24 h. The locomotive ability of C. elegans L4 worms was significantly reduced when treated with 40 μg/mL spectinabilin. Further analysis of spectinabilin against known nematicidal drug target genes in C. elegans showed that it acts via target(s) different from those of some currently used nematicidal drugs such as avermectin and phosphine thiazole. This is the first report on the nematicidal activity of spectinabilin on C. elegans and the southern root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita. These findings may pave the way for further research and application of spectinabilin as a potential biological nematicide.
Keywords: biological control; drug target; natural products; nematicide; plant parasitic nematode.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nematicidal effects of a peptidase (NlpC/P60) from the phytopathogen Pseudomonas syringae MB03 on the model nematode Caenorhabditis elegans and plant-parasitic Meloidogyne incognita.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):6313-6324. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07439-5. Epub 2022 May 9. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35532867
-
Synthesis, Nematicidal Evaluation, and the Structure-Activity Relationship Study of Aurone Derivatives.J Agric Food Chem. 2023 Jun 14;71(23):8757-8768. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c00627. Epub 2023 Jun 5. J Agric Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37277310
-
Harnessing nature's arsenal: Ochrobactrum bacteria metabolites in the battle against root- knot nematode - Insights from in vitro and molecular docking studies.J Invertebr Pathol. 2024 Jun;204:108114. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2024.108114. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Invertebr Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38636720
-
Whole-genome sequencing and analysis of Streptomyces strains producing multiple antinematode drugs.BMC Genomics. 2022 Aug 23;23(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08847-4. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35996099 Free PMC article.
-
Naturally-occurring nematicides of plant origin: two decades of novel chemistries.Pest Manag Sci. 2025 Feb;81(2):540-571. doi: 10.1002/ps.8504. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Pest Manag Sci. 2025. PMID: 39503300 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Interference with sexual mating of Sporisorium scitamineum by verrucarin A isolated from Paramyrothecium sp.Mycology. 2024 Nov 25;16(2):929-940. doi: 10.1080/21501203.2024.2426480. eCollection 2025. Mycology. 2024. PMID: 40415909 Free PMC article.
-
Natural products with γ-pyrone scaffold from Streptomyces.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 24;108(1):471. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13296-y. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39316232 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptomyces as a promising biological control agents for plant pathogens.Front Microbiol. 2023 Nov 14;14:1285543. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1285543. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38033592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Martinez-Servat S., Pinyol-Escala L., Daura-Pich O., Almazan M., Hernandez I., Lopez-Garcia B., Fernandez C. Characterization of Lysobacter enzymogenes B25, a potential biological control agent of plant-parasitic nematodes, and its mode of action. AIMS Microbiol. 2023;9:151–176. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2023010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

