Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of α-Synuclein Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras
- PMID: 37298935
- PMCID: PMC10254247
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28114458
Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of α-Synuclein Proteolysis-Targeting Chimeras
Abstract
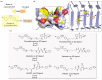
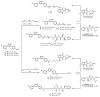
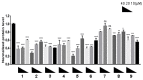
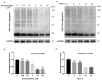
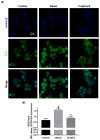
α-Synuclein aggregation under pathological conditions is one of the causes of related neurodegenerative diseases. PROTACs (proteolysis targeting chimeras) are bifunctional small molecules that induce a post-translational erasure of proteins via the ubiquitination of target proteins by E3 ubiquitin ligase and subsequent proteasomal degradation. However, few research studies have been conducted for targeted protein degradation of α-synuclein aggregates. In this article, we have designed and synthesized a series of small-molecule degraders 1-9 based on a known α-synuclein aggregation inhibitor sery384. In silico docking studies of sery384 with α-synuclein aggregates were accomplished to ensure that the compounds bound to α-synuclein aggregates specifically. The protein level of α-synuclein aggregates was determined to evaluate the degradation efficiency of PROTAC molecules on α-synuclein aggregates in vitro. The results show that compound 5 had the most significant degradation effect, with DC50 of 5.049 μM, and could induce the degradation of α-synuclein aggregates in a time- and dose-dependent manner in vitro. Furthermore, compound 5 could inhibit the elevation of the ROS level caused by overexpression and aggregation of α-synuclein and protect H293T cells from α-synuclein toxicity. Conclusively, our results provide a new class of small-molecule degraders and an experimental basis for the treatment of α-synuclein related neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: PROTAC (proteolysis-targeting chimera); protein aggregates; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dehay B., Bourdenx M., Gorry P., Przedborski S., Vila M., Hunot S., Singleton A., Olanow C.W., Merchant K.M., Bezard E., et al. Targeting α-synuclein for treatment of Parkinson’s disease: Mechanistic and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14:855–866. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00006-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

