Cinnamon Oil-Loaded Nanoliposomes with Potent Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities
- PMID: 37298980
- PMCID: PMC10254904
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28114492
Cinnamon Oil-Loaded Nanoliposomes with Potent Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Activities
Abstract
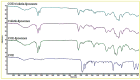
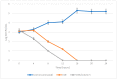
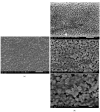
Despite recent scientific advances, the global load of bacterial disease remains high and has been established against a backdrop of increasing antimicrobial resistance. Therefore, there is a pressing need for highly effective and natural antibacterial agents. In the present work, the antibiofilm effect provided by essential oils was evaluated. Of these, cinnamon oil extract showed potent antibacterial and antibiofilm activities against Staphylococcus aureus at an MBEC of 75.0 µg/mL. It was revealed that benzyl alcohol, 2-propenal-3-phenyl, hexadecenoic acid, and oleic acid were the major components of the tested cinnamon oil extract. In addition, the interaction between the cinnamon oil and colistin showed a synergistic effect against S. aureus. Cinnamon oil that had been combined with colistin was encapsulated by liposomes to enhance the essential oil's chemical stability, demonstrating a particle size of 91.67 nm, a PDI of 0.143, a zeta potential of -0.129 mV, and an MBEC of 50.0 µg/mL against Staphylococcus aureus. Scanning electron microscopy was employed to observe the morphological changes in the Staphylococcus aureus biofilm that was treated with the encapsulated cinnamon oil extract/colistin. As a natural and safe option, cinnamon oil exhibited satisfactory antibacterial and antibiofilm performance. The application of liposomes further improved the stability of the antibacterial agents and extended the essential oil release profile.
Keywords: antibacterial; antibiofilm; cinnamon oil; colistin; combination study; nanoliposome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Liposome containing cinnamon oil with antibacterial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus biofilm.Biofouling. 2016;32(2):215-25. doi: 10.1080/08927014.2015.1134516. Biofouling. 2016. PMID: 26838161
-
In vitro anticariogenic and antibiofilm activities of toothpastes formulated with essential oils.Arch Oral Biol. 2020 Sep;117:104834. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104834. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Arch Oral Biol. 2020. PMID: 32663696
-
Synergistic interaction of clove, cinnamon, and eucalyptus essential oils impregnated in cellulose acetate electrospun fibers as antibacterial agents against Staphylococcus aureus.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Sep;54(3):1635-1643. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-01048-5. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37391674 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial mechanisms of cinnamon and its constituents: A review.Microb Pathog. 2018 Jul;120:198-203. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.036. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29702210 Review.
-
Effects of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum spp.) in Dentistry: A Review.Molecules. 2020 Sep 12;25(18):4184. doi: 10.3390/molecules25184184. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32932678 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and characteristics of carboxymethyl cellulose-based films embedding cinnamon essential oil and their application on mutton preservation.Front Nutr. 2025 Apr 30;12:1559833. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1559833. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40370803 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Essential-Oil-Based Nanostructured Lipid Carriers against Campylobacter Spp. Isolated from Chicken Carcasses.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 11;16(7):922. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070922. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065619 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Biofilm-Associated Infections and the Role of Phytochemicals and Nanomaterials in Their Control and Prevention.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jan 24;16(2):162. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020162. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Bacterial Biofilms: Formation, Impacts, and Possible Management Targets in the Healthcare System.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2024 Dec 16;2024:1542576. doi: 10.1155/cjid/1542576. eCollection 2024. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39717533 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cinnamon Essential Oil Delivery Systems: Preparation Processes, Packaging Forms, and Industrialization Potentials.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 29;13(9):e70814. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70814. eCollection 2025 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40895151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frozi J.B., Esper L.M.R., Franco R.M. Single-and multispecies biofilms by Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Salmonella spp. isolated from raw fish and a fish processing unit. Ciência Rural. 2017;47 doi: 10.1590/0103-8478cr20170011. - DOI
-
- Millezi A.F., Costa K.A.D., Oliveira J.M., Lopes S.P., Pereira M.O., Piccoli R.H. Atividade antibacteriana e anti-biofilme de óleo essencial de canela e eugenol. Ciência Rural. 2019;49 doi: 10.1590/0103-8478cr20180314. - DOI
-
- Rasool N., Saeed Z., Pervaiz M., Ali F., Younas U., Bashir R., Bukhari S.M., Khan R.R.M., Jelani S., Sikandar R. Evaluation of essential oil extracted from ginger, cinnamon and lemon for therapeutic and biological activities. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2022;44:102470. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2022.102470. - DOI
-
- Alam A. Herbs that heal spices: The hoard of natural remedies. Ann. Phytomed. 2019;8:7–18. doi: 10.21276/ap.2019.8.2.2. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

