Cardioprotective Properties of Kaempferol: A Review
- PMID: 37299076
- PMCID: PMC10255479
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12112096
Cardioprotective Properties of Kaempferol: A Review
Abstract
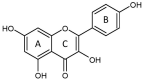
Cardiac diseases, such as myocardial infarction and heart failure, have become a major clinical problem globally. The accumulating data demonstrate that bioactive compounds with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties have favorable effects on clinical problems. Kaempferol is a flavonoid found in various plants; it has demonstrated cardioprotective properties in numerous cardiac injury models. This review aims to collate updated information regarding the effects of kaempferol on cardiac injury. Kaempferol improves cardiac function by alleviating myocardial apoptosis, fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation while preserving mitochondrial function and calcium homeostasis. However, the mechanisms of action of its cardioprotective properties remain unclear; therefore, elucidating its action could provide insight into directions for future studies.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antiapoptosis; antifibrosis; antioxidant; calcium regulation; cardiac disease; cardiac function; flavonoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Cardiovascular Diseases. [(accessed on 10 May 2023)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1.2023.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

