Transcriptional and Post-Translational Regulation of Plant bHLH Transcription Factors during the Response to Environmental Stresses
- PMID: 37299095
- PMCID: PMC10255293
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12112113
Transcriptional and Post-Translational Regulation of Plant bHLH Transcription Factors during the Response to Environmental Stresses
Abstract
Over the past decades, extensive research has been conducted to identify and characterize various plant transcription factors involved in abiotic stress responses. Therefore, numerous efforts have been made to improve plant stress tolerance by engineering these transcription factor genes. The plant basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor family represents one of the most prominent gene families and contains a bHLH motif that is highly conserved in eukaryotic organisms. By binding to specific positions in promoters, they activate or repress the transcription of specific response genes and thus affect multiple variables in plant physiology such as the response to abiotic stresses, which include drought, climatic variations, mineral deficiencies, excessive salinity, and water stress. The regulation of bHLH transcription factors is crucial to better control their activity. On the one hand, they are regulated at the transcriptional level by other upstream components; on the other hand, they undergo various modifications such as ubiquitination, phosphorylation, and glycosylation at the post-translational level. Modified bHLH transcription factors can form a complex regulatory network to regulate the expression of stress response genes and thus determine the activation of physiological and metabolic reactions. This review article focuses on the structural characteristics, classification, function, and regulatory mechanism of bHLH transcription factor expression at the transcriptional and post-translational levels during their responses to various abiotic stress conditions.
Keywords: abiotic stress; bHLH transcription factors; post-translational regulation; transcriptional regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
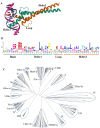

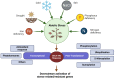


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

