Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum
- PMID: 37299110
- PMCID: PMC10255886
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12112131
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of WRKY Transcription Factors and Their Expression Profile in Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum
Abstract
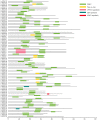
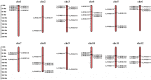
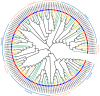
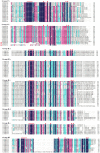
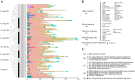
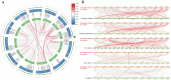
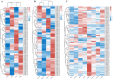
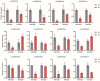
The WRKY gene family plays important roles in plant growth and development, as well as in the responses to biotic and abiotic stresses. Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum has high ornamental and medicinal value. However, few WRKY genes have been reported in this plant, and their functions remain unknown. To explore the roles that the WRKY genes play in L. chinense var. rubrum, we identified and characterized 79 LcWRKYs through BLAST homology analysis and renamed them (as LcWRKY1-79) based on their distribution on the chromosomes of L. chinense var. rubrum. In this way, according to their structural characteristics and phylogenetic analysis, they were divided into three groups containing 16 (Group I), 52 (Group II), and 11 (Group III) WRKYs, respectively. LcWRKYs in the same group have similar motifs and gene structures; for instance, Motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 10 constitute the WRKY domain and zinc-finger structure. The LcWRKY promoter region contains light response elements (ACE, G-box), stress response elements (TC-rich repeats), hormone response elements (TATC-box, TCA-element), and MYB binding sites (MBS, MBSI). Synteny analysis of LcWRKYs allowed us to establish orthologous relationships among the WRKY gene families of Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Solanum lycopersicum L., Vitis vinifera L., Oryza sativa L., and Zea mays L.; furthermore, analysis of the transcriptomes of mature leaves and flowers from different cultivars demonstrated the cultivar-specific LcWRKY gene expression. The expression levels of certain LcWRKY genes also presented responsive changes from young to mature leaves, based on an analysis of the transcriptome in leaves at different developmental stages. White light treatment led to a significant decrease in the expression of LcWRKY6, 18, 24, 34, 36, 44, 48, 61, 62, and 77 and a significant increase in the expression of LcWRKY41, blue light treatment led to a significant decrease in the expression of LcWRKY18, 34, 50, and 77 and a significant increase in the expression of LcWRKY36 and 48. These results enable a better understanding of LcWRKYs, facilitating the further exploration of their genetic functions and the molecular breeding of L. chinense var. rubrum.
Keywords: Loropetalum chinense var. rubrum; WRKY; expression pattern; genome-wide analysis; light quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
- 2021YYXK001/the Open Project of Horticulture Discipline of Hunan Agricultural University
- XLKJ202205/The Forestry Science and Technology Innovation Foundation of Hunan Province for Distinguished Young Scholarship
- 2130221/The Forestry Bureau for Industrialization management of Hunan Province
- 22A0155/Key project of Hunan Provincial Department of Education
- KQ2202227/The Found of Changsha Municipal Science and Technology Bureau
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

