Contrasting Responses and Phytoremediation Potential of Two Poplar Species to Combined Strontium and Diesel Oil Stress
- PMID: 37299124
- PMCID: PMC10255748
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12112145
Contrasting Responses and Phytoremediation Potential of Two Poplar Species to Combined Strontium and Diesel Oil Stress
Abstract
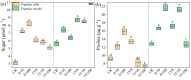
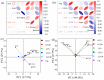
The soil pollution caused by diesel oil and heavy metals has become an increasingly serious environmental issue, with negative global-scale impacts. The remediation of contaminated soil requires special attention, in which phytoremediation has emerged as an ecofriendly solution. However, the response of plants to the combined stress of diesel oil and heavy metals remains largely unknown. In this study, the aim was to investigate the potential of Populus alba and P. russkii for phytoremediation by examining their response to combined diesel oil and heavy metal stress. In a greenhouse experiment using soil contaminated with 15 mg kg-1 of diesel oil and varying concentrations of Sr (0, 10, or 100 mg kg-1), we studied the physiological and biochemical changes, as well as the Sr absorption, of P. alba and P. russkii. The results showed that at high concentrations of Sr and diesel oil, the growth of both species was substantially inhibited, but P. alba exhibited higher resistance due to its higher antioxidant enzyme activities and increased accumulation of soluble sugar and proline. Additionally, P. alba concentrated Sr in the stem, whereas P. russkii accumulated Sr in the leaf, exacerbating its negative effects. Diesel oil treatments were beneficial for Sr extraction due to cross-tolerance. Our findings indicate that P. alba is more suitable for the phytoremediation of Sr contamination due to its superior tolerance to combined stress, and we identified potential biomarkers for monitoring pollution. Therefore, this study provides a theoretical basis and implementation strategy for the remediation of soil contaminated by both heavy metals and diesel oil.
Keywords: Populus; combined stress; cross tolerance; diesel oil; physiological response; phytoremediation; strontium.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Physiological Responses of Populus cathayana and Salix babylonica to Combined Stress of Diesel Fuel and Sr2+ Stress in Soil.Plants (Basel). 2024 Dec 23;13(24):3598. doi: 10.3390/plants13243598. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39771296 Free PMC article.
-
Lithium and strontium accumulation in native and invasive plants of the Sava River: Implications for bioindication and phytoremediation.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024 Jan 15;270:115875. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115875. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2024. PMID: 38142593
-
Physiological responses of Morus alba L. in heavy metal(loid)-contaminated soil and its associated improvement of the microbial diversity.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Feb;27(4):4294-4308. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-07124-4. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 31832962
-
Phytoremediation: role of terrestrial plants and aquatic macrophytes in the remediation of radionuclides and heavy metal contaminated soil and water.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Jan;22(2):946-62. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3635-8. Epub 2014 Oct 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25277712 Review.
-
Suitability of aromatic plants for phytoremediation of heavy metal contaminated areas: a review.Int J Phytoremediation. 2019;21(5):405-418. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2018.1540546. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Int J Phytoremediation. 2019. PMID: 30656974 Review.
Cited by
-
Populus × euramericana Accumulates More Organic Pollutants (PAHs and PCBs), While P. nigra 'Italica' Absorbs More Heavy Metals.Plants (Basel). 2025 May 12;14(10):1445. doi: 10.3390/plants14101445. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40431010 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiao W., Wang H., Li T., Zhu Z., Zhang J., He Z., Yang X. Bioremediation of Cd and carbendazim co-contaminated soil by Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii associated with carbendazim-degrading bacterial strains. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013;20:380–389. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-0902-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

