Improving Flavonoid Accumulation of Bioreactor-Cultured Adventitious Roots in Oplopanax elatus Using Yeast Extract
- PMID: 37299154
- PMCID: PMC10255709
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12112174
Improving Flavonoid Accumulation of Bioreactor-Cultured Adventitious Roots in Oplopanax elatus Using Yeast Extract
Abstract
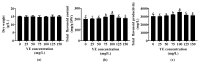
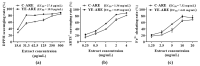
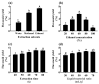
Oplopanax elatus is an endangered medicinal plant, and adventitious root (AR) culture is an effective way to obtain its raw materials. Yeast extract (YE) is a lower-price elicitor and can efficiently promote metabolite synthesis. In this study, the bioreactor-cultured O. elatus ARs were treated with YE in a suspension culture system to investigate the elicitation effect of YE on flavonoid accumulation, serving for further industrial production. Among YE concentrations (25-250 mg/L), 100 mg/L YE was the most suitable for increasing the flavonoid accumulation. The ARs with various ages (35-, 40-, and 45-day-old) responded differently to YE stimulation, where the highest flavonoid accumulation was found when 35-day-old ARs were treated with 100 mg/L YE. After YE treatment, the flavonoid content increased, peaked at 4 days, and then decreased. By comparison, the flavonoid content and antioxidant activities in the YE group were obviously higher than those in the control. Subsequently, the flavonoids of ARs were extracted by flash extraction, where the optimized extraction process was: 63% ethanol, 69 s of extraction time, and a 57 mL/g liquid-material ratio. The findings provide a reference for the further industrial production of flavonoid-enriched O. elatus ARs, and the cultured ARs have potential application for the future production of products.
Keywords: Oplopanax elatus; elicitation duration; elicitation time; elicitor concentration; flash extraction; yeast extract.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
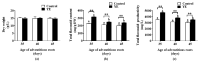



Similar articles
-
Optimizing elicitation strategy of salicylic acid for flavonoid and phenolic production of fed-batch cultured Oplopanax elatus adventitious roots.J Biotechnol. 2023 May 20;368:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2023.04.004. Epub 2023 Apr 17. J Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37075954
-
Adventitious root cultures of Oplopanax elatus inhibit LPS-induced inflammation via suppressing MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019 Oct;55(9):766-775. doi: 10.1007/s11626-019-00396-7. Epub 2019 Sep 16. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2019. PMID: 31529418
-
Effect of explant type (leaf, stem) and 2,4-D concentration on callus induction: influence of elicitor type (biotic, abiotic), elicitor concentration and elicitation time on biomass growth rate and costunolide biosynthesis in gazania (Gazania rigens) cell suspension cultures.Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022 Sep 16;9(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s40643-022-00588-2. Bioresour Bioprocess. 2022. PMID: 38647613 Free PMC article.
-
Elicitation of Submerged Adventitious Root Cultures of Stevia rebaudiana with Cuscuta reflexa for Production of Biomass and Secondary Metabolites.Molecules. 2021 Dec 21;27(1):14. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010014. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011247 Free PMC article.
-
Oplopanax elatus (Nakai) Nakai: chemistry, traditional use and pharmacology.Chin J Nat Med. 2014 Oct;12(10):721-9. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(14)60111-4. Epub 2014 Oct 31. Chin J Nat Med. 2014. PMID: 25443364 Review.
Cited by
-
Combined Metabolomics and Transcriptomics Analysis of the Distribution of Flavonoids in the Fibrous Root and Taproot of Polygonatum kingianum Coll.et Hemsl.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jun 22;15(7):828. doi: 10.3390/genes15070828. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062607 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang X.L., Jin M.Y., Piao X.C., Yin C.R., Lian M.L. Fed-batch culture of Oplopanax elatus adventitious roots: Feeding medium selection through comprehensive evaluation using an analytic hierarchy process. Biochem. Eng. J. 2021;167:107927. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2021.107927. - DOI
-
- Han L., Piao X.C., Jiang Y.J., Jiang X.L., Yin C.R., Lian M.L. A high production of flavonoids and anthraquinones via adventitious root culture of Oplopanax elatus and evaluating antioxidant activity. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2019;137:173–179. doi: 10.1007/s11240-018-01543-w. - DOI
-
- Jiang X.L., Piao X.C., Gao R., Jin M.Y., Jin X.H., Lian M.L. Improvement of bioactive compound accumulation in adventitious root cultures of an endangered plant species, Oplopanax elatus. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2017;39:226. doi: 10.1007/s11738-017-2525-3. - DOI
-
- Jiang Y.J., Piao X.C., Liu J.S., Lian Z.X., Kim M.J., Lian M.L. Bioactive compound production by adventitious root culture of Oplopanax elatus in balloon-type airlift bioreactor systems and bioactivity property. Plant Cell Tiss. Organ Cult. 2015;123:413–425. doi: 10.1007/s11240-015-0845-9. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

