Effect of Ornithine α-Ketoglutarate on Intestinal Microbiota and Serum Inflammatory Cytokines in Dextran Sulfate Sodium Induced Colitis
- PMID: 37299439
- PMCID: PMC10255407
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15112476
Effect of Ornithine α-Ketoglutarate on Intestinal Microbiota and Serum Inflammatory Cytokines in Dextran Sulfate Sodium Induced Colitis
Abstract
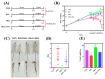
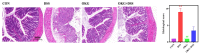
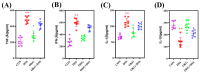
Ornithine α-ketoglutarate (OKG), a nutritional compound, is an amino acid salt with anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects on humans and animals. Ulcerative colitis (UC), as an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), leads to chronic intestinal inflammatory dysfunction. This study evaluated the optimal dosage of OKG in healthy mice. Then, a mouse model of acute colitis was established using dextran sodium sulfate (DSS), and the preventive effect of OKG on DSS-induced colitis in mice was explored through analysis of serum inflammatory cytokines and fecal microbiota. Initially, the mice were randomly divided into a control group, a group given a low dose of OKG (LOKG: 0.5%), a group given a medium dose of OKG (MOKG: 1%), and a group given a high dose of OKG (HOKG: 1.5%); they remained in these groups for the entire 14-day experimental period. Our results demonstrated that 1% OKG supplementation increased body weight, serum growth hormone (GH), insulin (INS), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), Tyr, and His and decreased urea nitrogen (BUN), NH3L, and Ile. Then, a 2 × 2 factor design was used for a total of 40 mice, with diet (a standard diet or a 1% OKG diet) and challenge (4% DSS or not) as the main factors. During days 14 to 21, the DSS mice were administered 4% DSS to induce colitis. The results revealed that OKG alleviated weight loss and reversed the increases in colonic histological damage induced by DSS. OKG also increased serum IL-10 secretion. Moreover, OKG enhanced the abundance of Firmicutes and decreased that of Bacteriodetes at the phylum level and particularly enhanced the abundance of Alistipes and reduced that of Parabacterioides at the genus level. Our results indicated that OKG promotes growth performance and hormone secretion and regulates serum biochemical indicators and amino acid concentrations. Furthermore, 1% OKG supplementation prevents DSS-induced colitis in mice via altering microbial compositions and reducing the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in serum.
Keywords: colitis; dextran sulfate sodium; inflammatory cytokines; intestinal microbiota; ornithine α-ketoglutarate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
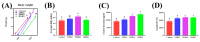
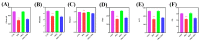
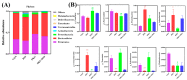
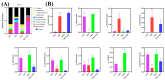
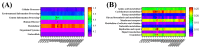
Similar articles
-
Sustained ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus LA85 on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice.J Food Sci. 2023 Sep;88(9):3893-3904. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.16723. Epub 2023 Aug 7. J Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 37548631
-
Lactobacillus salivarius alleviated dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in mice by mitigating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses through modulation of the intestinal flora.Microb Pathog. 2025 Aug;205:107696. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107696. Epub 2025 May 10. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40355053
-
2,3,5,4'-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-D-glucoside, a major bioactive component from Polygoni multiflori Radix (Heshouwu) suppresses DSS induced acute colitis in BALb/c mice by modulating gut microbiota.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 May;137:111420. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111420. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33761623
-
Unveiling Colitis: A Journey through the Dextran Sodium Sulfate-induced Model.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024 May 2;30(5):844-853. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad312. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2024. PMID: 38280217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A scoping review on reporting of methods in DSS colitis mouse models.Lab Anim. 2025 Jun 14:236772251331677. doi: 10.1177/00236772251331677. Online ahead of print. Lab Anim. 2025. PMID: 40515727 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering Microbial Composition in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Implications for Therapeutic Response to Biologic Agents.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 21;12(7):1260. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071260. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065032 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Reduced TCA Cycle Metabolite Levels in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Apr 16;18:5205-5216. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S487349. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40255656 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hernandez-Chirlaque C., Aranda C.J., Ocon B., Capitan-Canadas F., Ortega-Gonzalez M., Carrero J.J., Suarez M.D., Zarzuelo A., Sanchez de Medina F., Martinez-Augustin O. Germ-free and Antibiotic-treated Mice are Highly Susceptible to Epithelial Injury in DSS Colitis. J. Crohn’s Colitis. 2016;10:1324–1335. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw096. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- QYZDY-SSW-SMC008/Key Programs of frontier scientific research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences
- tscy20190121/TaiShan Industrial Experts Program
- 2021YFD1300402/National Key R&D Program of China
- 1610242022001-02/Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund
- kq2208249/Natural Science Foundation of Changsha Municipal
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

