Serum Essential Elements and Survival after Cancer Diagnosis
- PMID: 37299574
- PMCID: PMC10255054
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15112611
Serum Essential Elements and Survival after Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
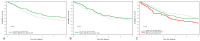
In a prospective study, we measured the associations between three serum elements (Se, Zn and Cu) and the prognosis of 1475 patients with four different types of cancer (breast, prostate, lung and larynx) from University Hospitals in Szczecin, Poland. The elements were measured in serum taken after diagnosis and prior to treatment. Patients were followed from the date of diagnosis until death from any cause or until the last follow-up date (mean years of follow-up: 6.0-9.8 years, according to site). Kaplan-Meier curves were constructed for all cancers combined and for each cancer separately. Age-adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) were estimated using Cox regression. The outcome was all-cause mortality. A Se level in the highest quartile was also associated with a reduced mortality (HR = 0.66; 95%CI 0.49-0.88; p = 0.005) in all-cause mortality for all cancers combined. Zn level in the highest quartile was also associated with reduced mortality (HR = 0.55; 95%CI 0.41-0.75; p = 0.0001). In contrast, a Cu level in the highest quartile was associated with an increase in mortality (HR = 1.91; 95%CI 1.56-2.08; p = 0.0001). Three serum elements-selenium, zinc and copper-are associated with the prognosis of different types of cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; copper; laryngeal cancer; lung cancer; prostate cancer; selenium; survival; zinc.
Conflict of interest statement
Jan Lubiński is the CEO of Read-Gene SA, which offers measurements on a micro-and macroelement level. These authors are part-time employees of Read-Gene: W.M., R.D., C.C., J.G. and T.H. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- de Jong V.M., Wang Y., ter Hoeve N.D., Opdam M., Stathonikos N., Jóźwiak K., Hauptmann M., Cornelissen S., Vreuls W., Rosenberg E.H., et al. Prognostic Value of Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Young, Node-Negative, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Who Did Not Receive (neo)Adjuvant Systemic Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:2361–2374. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01536. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

