Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds
- PMID: 37299623
- PMCID: PMC10254128
- DOI: 10.3390/nano13111720
Natural Cellulose-Based Multifunctional Nanofibers for the Effective Removal of Particulate Matter and Volatile Organic Compounds
Abstract
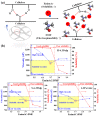
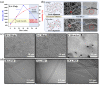
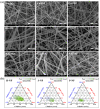
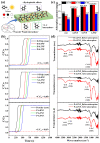
Multifunctional nanofibers for particulate matter (PM) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) removal from the indoor atmospheric environment were manufactured from eco-friendly natural cellulose materials via electrospinning using an optimized solvent system containing 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate (EmimAC) and dimethylformide (DMF) in a 3:7 volume ratio. EmimAC improved the cellulose stability, whereas DMF improved the electrospinnability of the material. Various cellulose nanofibers were manufactured using this mixed solvent system and characterized according to the cellulose type, such as hardwood pulp, softwood pulp, and cellulose powder, and cellulose content ranging from 6.0-6.5 wt%. The correlation between the precursor solution alignment and electrospinning properties indicated an optimal cellulose content of 6.3 wt% for all cellulose types. The hardwood pulp-based nanofibers possessed the highest specific surface area and exhibited high efficiency for eliminating both PM and VOCs, with a PM2.5 adsorption efficiency of 97.38%, PM2.5 quality factor of 0.28, and toluene adsorption of 18.4 mg/g. This study will contribute to the development of next-generation eco-friendly multifunctional air filters for indoor clean-air environments.
Keywords: air filter; cellulose; ionic liquid; nanofiber; toluene adsorption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Electrospun Fibers from Biobased and Recycled Materials for Indoor Air Quality Enhancement.Molecules. 2025 Mar 8;30(6):1214. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061214. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40141991 Free PMC article.
-
Sericin-coated polyester based air-filter for removal of particulate matter and volatile organic compounds (BTEX) from indoor air.Chemosphere. 2019 Dec;237:124462. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124462. Epub 2019 Jul 27. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31394446
-
Electrospun silk nanofiber loaded with Ag-doped TiO2 with high-reactive facet as multifunctional air filter.RSC Adv. 2023 Aug 29;13(37):25729-25737. doi: 10.1039/d3ra04621d. eCollection 2023 Aug 29. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37649664 Free PMC article.
-
Application of cellulose nanofiber as a promising air filter for adsorbing particulate matter and carbon dioxide.Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Jul 31;244:125344. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125344. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023. PMID: 37327938 Review.
-
Mitigation of indoor air pollution: A review of recent advances in adsorption materials and catalytic oxidation.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Mar 5;405:124138. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124138. Epub 2020 Oct 10. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 33092884 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrospun Fibers from Biobased and Recycled Materials for Indoor Air Quality Enhancement.Molecules. 2025 Mar 8;30(6):1214. doi: 10.3390/molecules30061214. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40141991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Navas-Martín M.Á., Oteiza I., Cuerdo-Vilches T. Dwelling in Times of COVID-19: An Analysis on Habitability and Environmental Factors of Spanish Housing. J. Build. Eng. 2022;60:105012. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.105012. - DOI
-
- Pui D.Y.H., Chen S.-C., Zuo Z. PM2.5 in China: Measurements, Sources, Visibility and Health Effects, and Mitigation. Particuology. 2014;13:1–26. doi: 10.1016/j.partic.2013.11.001. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

