Longitudinal Studies of Wearables in Patients with Diabetes: Key Issues and Solutions
- PMID: 37299733
- PMCID: PMC10255223
- DOI: 10.3390/s23115003
Longitudinal Studies of Wearables in Patients with Diabetes: Key Issues and Solutions
Abstract
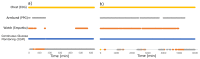
Glucose monitoring is key to the management of diabetes mellitus to maintain optimal glucose control whilst avoiding hypoglycemia. Non-invasive continuous glucose monitoring techniques have evolved considerably to replace finger prick testing, but still require sensor insertion. Physiological variables, such as heart rate and pulse pressure, change with blood glucose, especially during hypoglycemia, and could be used to predict hypoglycemia. To validate this approach, clinical studies that contemporaneously acquire physiological and continuous glucose variables are required. In this work, we provide insights from a clinical study undertaken to study the relationship between physiological variables obtained from a number of wearables and glucose levels. The clinical study included three screening tests to assess neuropathy and acquired data using wearable devices from 60 participants for four days. We highlight the challenges and provide recommendations to mitigate issues that may impact the validity of data capture to enable a valid interpretation of the outcomes.
Keywords: continuous blood glucose; data collection; diabetes management; longitudinal monitoring; machine learning; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Seneviratne S., Hu Y., Nguyen T., Lan G., Khalifa S., Thilakarathna K., Hassan M., Seneviratne A. A Survey of Wearable Devices and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017;19:2573–2620. doi: 10.1109/COMST.2017.2731979. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

