Challenges and Limitation Analysis of an IoT-Dependent System for Deployment in Smart Healthcare Using Communication Standards Features
- PMID: 37299881
- PMCID: PMC10255234
- DOI: 10.3390/s23115155
Challenges and Limitation Analysis of an IoT-Dependent System for Deployment in Smart Healthcare Using Communication Standards Features
Abstract
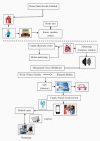
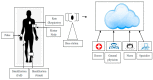
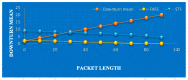
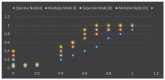
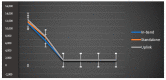
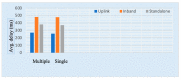
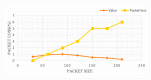
The use of IoT technology is rapidly increasing in healthcare development and smart healthcare system for fitness programs, monitoring, data analysis, etc. To improve the efficiency of monitoring, various studies have been conducted in this field to achieve improved precision. The architecture proposed herein is based on IoT integrated with a cloud system in which power absorption and accuracy are major concerns. We discuss and analyze development in this domain to improve the performance of IoT systems related to health care. Standards of communication for IoT data transmission and reception can help to understand the exact power absorption in different devices to achieve improved performance for healthcare development. We also systematically analyze the use of IoT in healthcare systems using cloud features, as well as the performance and limitations of IoT in this field. Furthermore, we discuss the design of an IoT system for efficient monitoring of various healthcare issues in elderly people and limitations of an existing system in terms of resources, power absorption and security when implemented in different devices as per requirements. Blood pressure and heartbeat monitoring in pregnant women are examples of high-intensity applications of NB-IoT (narrowband IoT), technology that supports widespread communication with a very low data cost and minimum processing complexity and battery lifespan. This article also focuses on analysis of the performance of narrowband IoT in terms of delay and throughput using single- and multinode approaches. We performed analysis using the message queuing telemetry transport protocol (MQTTP), which was found to be efficient compared to the limited application protocol (LAP) in sending information from sensors.
Keywords: IoT; cloud; communication standard; healthcare; security; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrating meta-heuristic with named data networking for secure edge computing in IoT enabled healthcare monitoring system.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 15;14(1):21532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71506-z. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39278954 Free PMC article.
-
Edge-Fog-Cloud Computing Hierarchy for Improving Performance and Security of NB-IoT-Based Health Monitoring Systems.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;22(22):8646. doi: 10.3390/s22228646. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433242 Free PMC article.
-
Remote Pain Monitoring Using Fog Computing for e-Healthcare: An Efficient Architecture.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Nov 18;20(22):6574. doi: 10.3390/s20226574. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33217896 Free PMC article.
-
Smart Home-based IoT for Real-time and Secure Remote Health Monitoring of Triage and Priority System using Body Sensors: Multi-driven Systematic Review.J Med Syst. 2019 Jan 15;43(3):42. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1158-z. J Med Syst. 2019. PMID: 30648217
-
Internet of things (IoT) applications for elderly care: a reflective review.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021 Apr;33(4):855-867. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01545-9. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021. PMID: 32277435 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing a Health Support System to Promote Care for the Elderly.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Jan 14;25(2):455. doi: 10.3390/s25020455. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39860825 Free PMC article.
-
An adaptive data-driven architecture for mental health care applications.PeerJ. 2024 Mar 29;12:e17133. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17133. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38563009 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mohit K., Kumar A., Verma S., Bhattacharya P., Ghimire D., Kim S.-H., Hosen A.S. Healthcare Internet of Things (H-IoT): Current Trends, Future Prospects, Applications, Challenges, and Security Issues. Electronics. 2023;12:2050.
-
- Perrier E. Positive Disruption: Healthcare, Ageing & Participation in the Age of Technology. The McKell Institute; Sydney, NSW, Australia: 2015.
-
- Gope P., Hwang T. BSN-Care: A Secure IoT Based Modern Healthcare System Using Body Sensor Network. IEEE Sens. J. 2016;16:1368–1376. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2502401. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

