Improved Spectrum Coexistence in 2.4 GHz ISM Band Using Optimized Chaotic Frequency Hopping for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Signals
- PMID: 37299909
- PMCID: PMC10255637
- DOI: 10.3390/s23115183
Improved Spectrum Coexistence in 2.4 GHz ISM Band Using Optimized Chaotic Frequency Hopping for Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Signals
Abstract
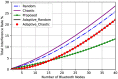
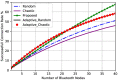
Efficiently managing coexistence is crucial for achieving high-quality wireless communication in the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) band where multiple wireless communication systems operate. Coexistence problems between Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) signals are especially significant due to their shared frequency band, which often leads to interference and a reduced performance for both systems. Therefore, effective coexistence management strategies are essential for ensuring the optimal performance of Wi-Fi and Bluetooth signals in the ISM band. In this paper, the authors conducted a study to investigate coexistence management in the ISM band by evaluating four frequency hopping techniques: random, chaotic, adaptive, and an optimized chaotic technique proposed by the authors. The optimized chaotic technique aimed to minimize interference and ensure zero self-interference among hopping BLE nodes by optimizing the update coefficient. Simulations were conducted in an environment with existing Wi-Fi signal interference and interfering Bluetooth nodes. The authors compared several performance metrics, including the total interference rate, total successful connection rate, and trial execution time for channel selection processing time. The results indicated that the proposed optimized chaotic frequency hopping technique achieved a better balance between reducing interference with Wi-Fi signals, achieving a high success rate for connecting BLE nodes, and requiring minimal trial execution time. This makes it a suitable technique for managing interference in wireless communication systems. While the proposed technique had a higher interference than the adaptive technique for small numbers of BLE nodes, for larger numbers of nodes it had a much lower interference than the adaptive technique. The proposed optimized chaotic frequency hopping technique provides a promising solution for effectively managing coexistence in the ISM band, particularly between Wi-Fi and BLE signals. It has the potential to improve the performance and quality of wireless communication systems.
Keywords: BLE; ISM band; Wi-Fi; frequency hopping; logistic map; spectrum coexistence.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Xu T., Zhang M., Zeng Y., Hu H. Harmonious coexistence of heterogeneous wireless networks in unlicensed bands: Solutions from the statistical signal transmission technique. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2019;14:61–69. doi: 10.1109/MVT.2019.2891790. - DOI
-
- Hassan W.A., Jo H.S., Ikki S., Nekovee M. Spectrum-Sharing Method for Co-Existence between 5G OFDM-Based System and Fixed. IEEE Access. 2019;7:77460–77475. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921973. - DOI
-
- Zhan S.C., Chou C.T., Chang S.C. Auction-based Spectrum Sharing Among Heterogeneous Secondary Networks; Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC); London, UK. 8–12 June 2015.
-
- Abass A.A.A., Kumbhkar R., Mandayam N.B., Gajic Z. WiFi/LTE-U coexistence: An evolutionary game approach. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2019;5:44–58. doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2886011. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

