Recent Developments in Inertial and Centrifugal Microfluidic Systems along with the Involved Forces for Cancer Cell Separation: A Review
- PMID: 37300027
- PMCID: PMC10256097
- DOI: 10.3390/s23115300
Recent Developments in Inertial and Centrifugal Microfluidic Systems along with the Involved Forces for Cancer Cell Separation: A Review
Abstract
The treatment of cancers is a significant challenge in the healthcare context today. Spreading circulating tumor cells (CTCs) throughout the body will eventually lead to cancer metastasis and produce new tumors near the healthy tissues. Therefore, separating these invading cells and extracting cues from them is extremely important for determining the rate of cancer progression inside the body and for the development of individualized treatments, especially at the beginning of the metastasis process. The continuous and fast separation of CTCs has recently been achieved using numerous separation techniques, some of which involve multiple high-level operational protocols. Although a simple blood test can detect the presence of CTCs in the blood circulation system, the detection is still restricted due to the scarcity and heterogeneity of CTCs. The development of more reliable and effective techniques is thus highly desired. The technology of microfluidic devices is promising among many other bio-chemical and bio-physical technologies. This paper reviews recent developments in the two types of microfluidic devices, which are based on the size and/or density of cells, for separating cancer cells. The goal of this review is to identify knowledge or technology gaps and to suggest future works.
Keywords: cancer diagnosis; cancer metastasis; cell enrichment; circulating tumor cells (CTCs); lab-on-a-CD (LOCD); lab-on-a-chip (LOC); microfluidic-based cell separation approaches.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures






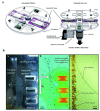

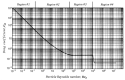
References
-
- Babikr F., Wan J., Xu A., Wu Z., Ahmed S., Freywald A., Chibbar R., Wu Y., Moser M., Groot G. Distinct roles but cooperative effect of TLR3/9 agonists and PD-1 blockade in converting the immunotolerant microenvironment of irreversible electroporation-ablated tumors. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021;18:2632–2647. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00796-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xu A., Zhang L., Yuan J., Babikr F., Freywald A., Chibbar R., Moser M., Zhang W., Zhang B., Fu Z. TLR9 agonist enhances radiofrequency ablation-induced CTL responses, leading to the potent inhibition of primary tumor growth and lung metastasis. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2019;16:820–832. doi: 10.1038/s41423-018-0184-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ding L., Fang Z., Moser M.A., Zhang W., Zhang B. A Single-Cell Electroporation Model for Quantitatively Estimating the Pore Area Ratio by High-Frequency Irreversible Electroporation. Appl. Sci. 2023;13:1808. doi: 10.3390/app13031808. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

