Dynamic Evaluation of the Degradation Process of Vibration Performance for Machine Tool Spindle Bearings
- PMID: 37300052
- PMCID: PMC10255970
- DOI: 10.3390/s23115325
Dynamic Evaluation of the Degradation Process of Vibration Performance for Machine Tool Spindle Bearings
Abstract
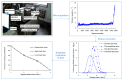
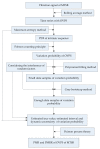
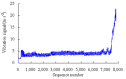
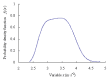
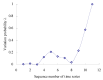
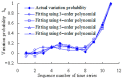
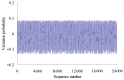
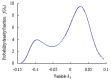
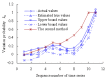
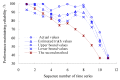
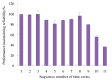
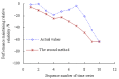
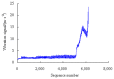
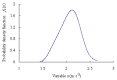
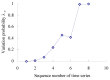
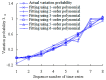
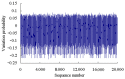
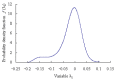
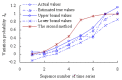
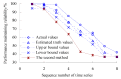
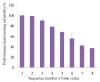
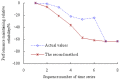
Real-time condition monitoring and fault diagnosis of spindle bearings are critical to the normal operation of the matching machine tool. In this work, considering the interference of random factors, the uncertainty of the vibration performance maintaining reliability (VPMR) is introduced for machine tool spindle bearings (MTSB). The maximum entropy method and Poisson counting principle are combined to solve the variation probability, so as to accurately characterize the degradation process of the optimal vibration performance state (OVPS) for MTSB. The dynamic mean uncertainty calculated using the least-squares method by polynomial fitting, fused into the grey bootstrap maximum entropy method, is utilized to evaluate the random fluctuation state of OVPS. Then, the VPMR is calculated, which is used to dynamically evaluate the failure degree of accuracy for MTSB. The results show that the maximum relative errors between the estimated true value and the actual value of the VPMR are 6.55% and 9.91%, and appropriate remedial measures should be taken before 6773 min and 5134 min for the MTSB in Case 1 and Case 2, respectively, so as to avoid serious safety accidents that are caused by the failure of OVPS.
Keywords: degradation probability; machine tool spindle bearings; optimal performance state; uncertainty; vibration performance maintaining reliability.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Liu J. A dynamic modelling method of a rotor-roller bearing-housing system with a localized fault including the additional excitation zone. J. Sound Vib. 2020;469:115144. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2019.115144. - DOI
-
- Zhang W.H., Deng S.E., Zhang S., Wang J., Zheng J.T. Abnormal wear mechanism and improvement of high-speed cylindrical roller bearing. Shock Vib. 2021;2021:2522386. doi: 10.1155/2021/2522386. - DOI
-
- Liu J., Xu Y., Pan G. A combined acoustic and dynamic model of a defective ball bearing. J. Sound Vib. 2021;501:116029. doi: 10.1016/j.jsv.2021.116029. - DOI
-
- Nataraj C., Harsha S.P. The effect of bearing cage run-out on the nonlinear dynamics of a rotating shaft. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. 2008;13:822–838. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2006.07.010. - DOI
-
- Xia X.T. Reliability analysis of zero-failure data with poor information. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2012;28:981–990. doi: 10.1002/qre.1279. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

