Genomic surveillance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Burundi, from May 2021 to January 2022
- PMID: 37301830
- PMCID: PMC10257533
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09420-3
Genomic surveillance of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in Burundi, from May 2021 to January 2022
Abstract
Background: The emergence and rapid spread of new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) variants have challenged the control of the COVID-19 pandemic globally. Burundi was not spared by that pandemic, but the genetic diversity, evolution, and epidemiology of those variants in the country remained poorly understood. The present study sought to investigate the role of different SARS-COV-2 variants in the successive COVID-19 waves experienced in Burundi and the impact of their evolution on the course of that pandemic. We conducted a cross-sectional descriptive study using positive SARS-COV-2 samples for genomic sequencing. Subsequently, we performed statistical and bioinformatics analyses of the genome sequences in light of available metadata.
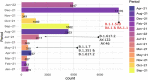
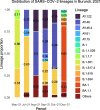
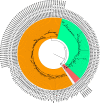
Results: In total, we documented 27 PANGO lineages of which BA.1, B.1.617.2, AY.46, AY.122, and BA.1.1, all VOCs, accounted for 83.15% of all the genomes isolated in Burundi from May 2021 to January 2022. Delta (B.1.617.2) and its descendants predominated the peak observed in July-October 2021. It replaced the previously predominant B.1.351 lineage. It was itself subsequently replaced by Omicron (B.1.1.529, BA.1, and BA.1.1). Furthermore, we identified amino acid mutations including E484K, D614G, and L452R known to increase infectivity and immune escape in the spike proteins of Delta and Omicron variants isolated in Burundi. The SARS-COV-2 genomes from imported and community-detected cases were genetically closely related.
Conclusion: The global emergence of SARS-COV-2 VOCs and their subsequent introductions in Burundi was accompanied by new peaks (waves) of COVID-19. The relaxation of travel restrictions and the mutations occurring in the virus genome played an important role in the introduction and the spread of new SARS-COV-2 variants in the country. It is of utmost importance to strengthen the genomic surveillance of SARS-COV-2, enhance the protection by increasing the SARS-COV-2 vaccine coverage, and adjust the public health and social measures ahead of the emergence or introduction of new SARS-COV-2 VOCs in the country.
Keywords: Amino acid change; COVID-19; Genetic diversity; Lineage; SARS-COV-2 variants; Waves.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic diversity and genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 during the first 3 years of the pandemic in Morocco: comprehensive sequence analysis, including the unique lineage B.1.528 in Morocco.Access Microbiol. 2024 Oct 7;6(10):000853.v4. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000853.v4. eCollection 2024. Access Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39376591 Free PMC article.
-
Emergency SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern: Novel Multiplex Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for Rapid Detection and Surveillance.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Feb 23;10(1):e0251321. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02513-21. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35196812 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Dynamics of Omicron (BA.1, BA.2, and BA.5) Waves and Emergence of the Deltacton Variant: Genomic Epidemiology of the SARS-CoV-2 Epidemic in Cyprus (Oct 2021-Oct 2022).Viruses. 2023 Sep 15;15(9):1933. doi: 10.3390/v15091933. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37766339 Free PMC article.
-
The outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages, immune escape, and vaccine effectivity.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28138. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28138. Epub 2022 Sep 21. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36097349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular evolution of SARS-CoV-2 from December 2019 to August 2022.J Med Virol. 2023 Jan;95(1):e28366. doi: 10.1002/jmv.28366. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 36458547 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO. COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update 2023. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on.... Cited 22 Apr 2023.
-
- WHO. COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update: 28 December 2021. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/350973. Cited 22 Apr 2023.
-
- Ministry of Public Health and the Fight against AIDS . Report on the Epidemiological Situation of COVID-19 in Burundi 2021. 2021.
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

