Generalized precursor prediction boosts identification rates and accuracy in mass spectrometry based proteomics
- PMID: 37301900
- PMCID: PMC10257694
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-04977-x
Generalized precursor prediction boosts identification rates and accuracy in mass spectrometry based proteomics
Abstract
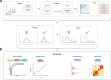
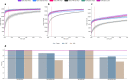
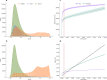
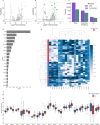
Data independent acquisition mass spectrometry (DIA-MS) has recently emerged as an important method for the identification of blood-based biomarkers. However, the large search space required to identify novel biomarkers from the plasma proteome can introduce a high rate of false positives that compromise the accuracy of false discovery rates (FDR) using existing validation methods. We developed a generalized precursor scoring (GPS) method trained on 2.75 million precursors that can confidently control FDR while increasing the number of identified proteins in DIA-MS independent of the search space. We demonstrate how GPS can generalize to new data, increase protein identification rates, and increase the overall quantitative accuracy. Finally, we apply GPS to the identification of blood-based biomarkers and identify a panel of proteins that are highly accurate in discriminating between subphenotypes of septic acute kidney injury from undepleted plasma to showcase the utility of GPS in discovery DIA-MS proteomics.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures

Similar articles
-
Micro-Data-Independent Acquisition for High-Throughput Proteomics and Sensitive Peptide Mass Spectrum Identification.Anal Chem. 2018 Aug 7;90(15):8905-8911. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b01026. Epub 2018 Jul 23. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29984981
-
An enhanced label-free proteomics approach for deep-diving into equine plasma proteome, including the discovery of protein biomarkers for strenuous exercise.Drug Test Anal. 2024 Aug;16(8):841-854. doi: 10.1002/dta.3606. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Drug Test Anal. 2024. PMID: 37986675
-
High-throughput, in-depth and estimated absolute quantification of plasma proteome using data-independent acquisition/mass spectrometry ("HIAP-DIA").Proteomics. 2021 Mar;21(5):e2000264. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202000264. Epub 2021 Feb 23. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 33460299
-
Multiplexed and data-independent tandem mass spectrometry for global proteome profiling.Mass Spectrom Rev. 2014 Nov-Dec;33(6):452-70. doi: 10.1002/mas.21400. Epub 2013 Nov 26. Mass Spectrom Rev. 2014. PMID: 24281846 Review.
-
Technical advances in proteomics: new developments in data-independent acquisition.F1000Res. 2016 Mar 31;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-419. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.7042.1. eCollection 2016. F1000Res. 2016. PMID: 27092249 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of false discovery rate control in tandem mass spectrometry analysis using entrapment.Nat Methods. 2025 Jul;22(7):1454-1463. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02719-x. Epub 2025 Jun 16. Nat Methods. 2025. PMID: 40524023 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of false discovery rate control in tandem mass spectrometry analysis using entrapment.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 21:2024.06.01.596967. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.01.596967. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Nat Methods. 2025 Jul;22(7):1454-1463. doi: 10.1038/s41592-025-02719-x. PMID: 38895431 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Unravelling potential biomarkers for acute and chronic brucellosis through proteomic and bioinformatic approaches.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jul 13;13:1216176. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1216176. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37520434 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting biologically informed neural networks for enhanced proteomic biomarker discovery and pathway analysis.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 2;14(1):5359. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41146-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37660105 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

