Bayesian risk prediction model for colorectal cancer mortality through integration of clinicopathologic and genomic data
- PMID: 37301916
- PMCID: PMC10257677
- DOI: 10.1038/s41698-023-00406-8
Bayesian risk prediction model for colorectal cancer mortality through integration of clinicopathologic and genomic data
Abstract
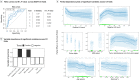
Routine tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging of colorectal cancer is imperfect in predicting survival due to tumor pathobiological heterogeneity and imprecise assessment of tumor spread. We leveraged Bayesian additive regression trees (BART), a statistical learning technique, to comprehensively analyze patient-specific tumor characteristics for the improvement of prognostic prediction. Of 75 clinicopathologic, immune, microbial, and genomic variables in 815 stage II-III patients within two U.S.-wide prospective cohort studies, the BART risk model identified seven stable survival predictors. Risk stratifications (low risk, intermediate risk, and high risk) based on model-predicted survival were statistically significant (hazard ratios 0.19-0.45, vs. higher risk; P < 0.0001) and could be externally validated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data (P = 0.0004). BART demonstrated model flexibility, interpretability, and comparable or superior performance to other machine-learning models. Integrated bioinformatic analyses using BART with tumor-specific factors can robustly stratify colorectal cancer patients into prognostic groups and be readily applied to clinical oncology practice.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
A.T.C. previously served as a consultant for Bayer Healthcare and Pfizer Inc. M.G. receives research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Servier and Janssen. C.S.F. is currently employed by Genentech / Roche and previously served as a consultant for Agios, Bain Capital, Bayer, Celgene, Dicerna, Five Prime Therapeutics, Gilead Sciences, Eli Lilly, Entrinsic Health, Genentech, KEW, Merck, Merrimack Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc, Sanofi, Taiho, and Unum Therapeutics; C.S.F. also serves as a Director for CytomX Therapeutics and owns unexercised stock options for CytomX and Entrinsic Health. R.N. is currently employed by Pfizer Inc.; she contributed to this study before she became an employee of Pfizer Inc. J.A.M. has received institutional research funding from Boston Biomedical, has served as an advisor/consultant to Ignyta and COTA Healthcare, and served on a grant review panel for the National Comprehensive Cancer Network funded by Taiho Pharmaceutical. This study was not funded by any of these commercial entities. K.-H.Y. is an inventor of U.S. Patent 10,832,406 (not related to this study). This study was not funded by any of these companies. C.G. is, as of November 2022, a postdoctoral research scientist at Columbia University of New York City and a part-time bioinformatician at Watershed Informatics. No other conflicts of interest exist. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
- R35 CA197735/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA087969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248857/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA225655/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA137178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 DK098311/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA205406/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM142879/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA151993/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 CA252962/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA186107/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA188126/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA167552/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

