Determination of aquatic hazard concentrations for the oil spill response product class of surface washing agents using species sensitivity distributions
- PMID: 37302201
- PMCID: PMC10870308
- DOI: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2023.115063
Determination of aquatic hazard concentrations for the oil spill response product class of surface washing agents using species sensitivity distributions
Abstract
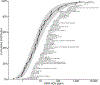
Surface washing agents (SWAs) are a diverse class of oil spill response products intended to facilitate removal of stranded oil from shorelines. This class of agents has high application rates relative to other categories of spill response products, but global toxicity data is generally limited to two standard test species: inland silverside and mysid shrimp. Here, we provide a framework to maximize the utility of limited toxicity data across a product class. To characterize species sensitivity to SWAs, the toxicity of three agents spanning a range of chemical and physical properties were tested in eight species. The relative sensitivity of mysids shrimp and inland silversides as surrogate test organisms was determined. Toxicity normalized species sensitivity distributions (SSDn) were used to estimate fifth centile hazard concentration (HC5) values for SWAs with limited toxicity data. Chemical toxicity distributions (CTD) of SWA HC5 values were used to compute a fifth centile chemical hazard distribution (HD5) to provide a more comprehensive assessment of hazard across a spill response product class with limited toxicity data than traditional single species or single agent approaches can give.
Keywords: Chemical toxicity distribution; Hazard concentration; Species sensitivity distribution; Surface washing agent; Toxicity.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
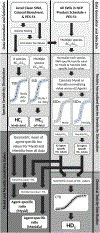
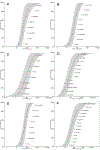
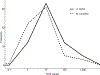
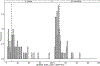
References
-
- Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council, 2000. Australian and New Zealand Guidelines for Fresh and Marine Water Quality. Australian and New Zealand Environment and Conservation Council and Agriculture and Resource Management Council of Australia and New Zealand, pp. 1–103.
-
- Barron MG, Hemmer MJ, Jackson CR, 2013. Development of aquatic toxicity benchmarks for oil products using species sensitivity distributions. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 9 (4), 610–615. - PubMed
-
- Baxter SME, DeLorenzo ME, Key PB, Chung KW, Pisarski E, Beckingham B, Fulton MH, 2018. Toxicity comparison of the shoreline cleaners Accell Clean® and PES-51® in two life stages of the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 25, 10926–10936. 10.1007/s11356-018-1370-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bejarano AC, 2018. Critical review and analysis of aquatic toxicity data on oil spill dispersants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 37 (12), 2989–3001. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

