Gastroparesis: Myths, Misconceptions, and Management
- PMID: 37303313
- PMCID: PMC10257400
- DOI: 10.2147/CEG.S362879
Gastroparesis: Myths, Misconceptions, and Management
Abstract
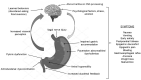
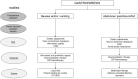
Gastroparesis (GP), a historically vexing disorder characterized by symptoms of nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, early satiety, and/or bloating, in the setting of an objective delay in gastric emptying, is often difficult to treat and carries a tremendous burden on the quality of patients' lives, as well as the healthcare system in general. Though the etiology of GP has been fairly well defined, much work has been done recently to better understand the pathophysiology of GP, as well as to identify novel effective and safe treatment options. As our understanding of GP has evolved, many myths and misconceptions still abound in this rapidly changing field. The goal of this review is to identify myths and misconceptions regarding the etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of GP, in the context of the latest research findings which have shaped our current understanding of GP. Recognition and dispelling of such myths and misconceptions is critical to moving the field forward and ultimately advancing the clinical management of what will hopefully become a better understood and more manageable disorder in the future.
Keywords: abdominal pain; functional dyspepsia; gastroparesis; nausea; vomiting.
© 2023 Cangemi and Lacy.
Conflict of interest statement
BEL is consultant for Ironwood, Urovant, Salix, Sanofi. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gastric electrical stimulation: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006;6(16):1-79. Epub 2006 Aug 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2006. PMID: 23074486 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroparesis Updates on Pathogenesis and Management.Gut Liver. 2017 Sep 15;11(5):579-589. doi: 10.5009/gnl16336. Gut Liver. 2017. PMID: 28535580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gastroparesis: The Complex Interplay with Microbiota and the Role of Exogenous Infections in the Pathogenesis of the Disease.Microorganisms. 2023 Apr 25;11(5):1122. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11051122. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37317096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical presentation and pathophysiology of gastroparesis.Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015 Mar;44(1):21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2014.11.003. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015. PMID: 25667020 Review.
-
Gastroparesis: A Review of Current Diagnosis and Treatment Options.J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug;49(7):550-8. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000320. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25874755 Review.
Cited by
-
Precision Endoscopy in Peroral Myotomies for Motility Disorders of the Upper Gastrointestinal Tract: Current Insights and Prospective Avenues-A Comprehensive Review.Life (Basel). 2023 Oct 31;13(11):2143. doi: 10.3390/life13112143. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38004283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials