Protective effects of Chinese herbal monomers against ischemia-reperfusion injury
- PMID: 37303663
- PMCID: PMC10250973
Protective effects of Chinese herbal monomers against ischemia-reperfusion injury
Abstract
Objectives: Ischemia-reperfusion injury is a complicated pathologic process that involves multiple factors including oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, calcium overload, inflammatory response, disturbances in energy metabolism, apoptosis, and some newly-described forms of programmed cell death (e.g., necroptosis, autophagy, pyroptosis, patanatos, and ferroptosis). Chinese herbal monomers (CHMs) have long been applied to treat ischemia-reperfusion injury based on a solid research foundation. This paper objectively reviews in vitro and in vivo studies on the use of CHMs to protect against ischemia-reperfusion injury.
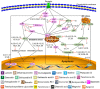
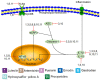
Methods: We reviewed 31 CHMs that have been shown to be effective for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury models of the heart, brain, and kidney. According to the mechanism of action, these CHMs were divided into three categories: protecting damaged histocytes, inhibiting inflammatory cells, and promoting the proliferation of damaged histocytes. Some CHMs were found to have more than one mechanism at the same time.
Results: Of the 31 CHMs, 28 protect damaged histocytes, 13 inhibit inflammatory cells, and three promote the proliferation of damaged histocytes.
Conclusions: CHMs show promise for treating ischemia-reperfusion injury. The eexisting treatment experiences for ischemia-reperfusion injury can be used as a reference.
Keywords: Chinese herbal monomers; cerebral infarction; ischemia-reperfusion injury; myocardial infarction; renal transplantation.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Rai AT, Seldon AE, Boo S, Link PS, Domico JR, Tarabishy AR, Lucke-Wold N, Carpenter JS. A population-based incidence of acute large vessel occlusions and thrombectomy eligible patients indicates significant potential for growth of endovascular stroke therapy in the USA. J Neurointerv Surg. 2017;9:722–726. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hilbert T, Klaschik S. The angiopoietin/TIE receptor system: focusing its role for ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015;26:281–291. - PubMed
-
- Chen C, Yu LT, Cheng BR, Xu JL, Cai Y, Jin JL, Feng RL, Xie L, Qu XY, Li D, Liu J, Li Y, Cui XY, Lu JJ, Zhou K, Lin Q, Wan J. Promising therapeutic candidate for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury: what are the possible mechanisms and roles of phytochemicals. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:792592. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
