Efficacy and safety of anterior capsule polishing in cataract patients: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 37303670
- PMCID: PMC10250971
Efficacy and safety of anterior capsule polishing in cataract patients: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This research summarizes and analyzes the effects of polishing of the anterior capsule (PAC) on visual function, maintenance of effective lens position (ELP), and postoperative complications in various studies, so as to determine whether PAC can be used to improve the surgical outcome of cataracts.
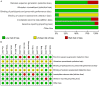
Methods: The literature related to PAC published before June 2022 was searched in PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, Cochrane, Google, Wanfang, Weipu and CNKI databases. Changes in visual function [uncorrected visual acuity (UCVA) and spherical equivalent refraction (SER)], effective lens position (ELP), and postoperative complications [anterior capsular opacification (ACO) and posterior capsular opacification (PCO)] in the PAC intervention group were summarized and analyzed, and the standardized mean difference (SMD) or odds ratio (OR) with 95% CI was calculated by Review Manager 5.3.
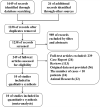
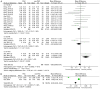
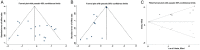
Results: By screening the literature, this meta-analysis finally included 10 studies with 2,639 eyes. The UCVA of patients was significantly improved in the PAC intervention group, while the root mean square of ELP (ELPRMS) level and ACO incidence decreased. In addition, PAC did not obviously reduce the incidence of PCO after cataract surgery.
Conclusion: PAC can effectively maintain the axial stability of the implanted lens and reduce the possibility of developing ACO, thus improving patients' visual function, which can effectively improve both the efficacy and safety of cataract surgery.
Keywords: Polishing of anterior capsule; capsular opacification; intraocular lens; meta-analysis; visual function.
AJTR Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Phakic intraocular lenses for the treatment of refractive errors: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009;9(14):1-120. Epub 2009 Oct 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2009. PMID: 23074518 Free PMC article.
-
Posterior capsular vacuuming to avoid PCO formation.Int Ophthalmol. 2022 Oct;42(10):3089-3095. doi: 10.1007/s10792-022-02295-5. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Int Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35378639
-
Impact of anterior capsular polishing on capsule opacification rate in eyes undergoing femtosecond laser-assisted cataract surgery.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020 May;68(5):780-785. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1787_19. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32317445 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of hydrophobic and hydrophilic intraocular lens in preventing posterior capsule opacification after cataract surgery: An updated meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Nov;96(44):e8301. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008301. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29095259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress of Drug Prophylaxis for Lens Capsule Opacification after Cataract Surgery.J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jul 4;2020:2181685. doi: 10.1155/2020/2181685. eCollection 2020. J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32714607 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring anterion capsular contraction syndrome in cataract surgery: insights into pathogenesis, clinical course, influencing factors, and intervention approaches.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Feb 19;11:1366576. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1366576. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38439904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Indications and outcomes of intraocular lens exchange at a tertiary ophthalmic center in Northern China from 2016 to 2024.Sci Rep. 2025 May 20;15(1):17422. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02573-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40394285 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Petternel V, Menapace R, Findl O, Kiss B, Wirtitsch M, Rainer G, Drexler W. Effect of optic edge design and haptic angulation on postoperative intraocular lens position change. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004;30:52–57. - PubMed
-
- Bolz M, Menapace R, Findl O, Sacu S, Buehl W, Wirtitsch M, Leydolt C, Kriechbaum K. Effect of anterior capsule polishing on the posterior capsule opacification-inhibiting properties of a sharp-edged, 3-piece, silicone intraocular lens: three- and 5-year results of a randomized trial. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2006;32:1513–1520. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
