The impact of bilingualism in within-language conflict resolution: an ERP study
- PMID: 37303909
- PMCID: PMC10248526
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1173486
The impact of bilingualism in within-language conflict resolution: an ERP study
Abstract
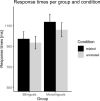
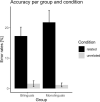
We compared Spanish (L1)-English (L2) bilinguals and Spanish monolinguals in a semantic judgment relationship task in L1 that produced within-language conflict due to the coactivation of the two meanings of a Spanish homophone (e.g., "hola" and "ola" meaning "hello" and "a wave" in English). In this task, participants indicated if pairs of words were related or not ("agua-hola," "water-hello"). Conflict arose because a word ("agua," "water") not related to the orthographic form of a homophone ("hola," "hello") was related to the alternative orthographic form ("ola," "wave"). Compared to a control condition with unrelated word pairs ("peluche-hola," "teddy-hello"), the behavioral results revealed greater behavioral interference in monolinguals compared to bilinguals. In addition, electrophysiological results revealed N400 differences between monolinguals and bilinguals. These results are discussed around the impact of bilingualism on conflict resolution.
Keywords: bilingualism; cognitive control; conflict resolution; inhibition; within-language conflict.
Copyright © 2023 Andras, Ramos and Macizo.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
On Language and Thought: Bilingual Experience Influences Semantic Associations.J Neurolinguistics. 2020 Nov;56:100932. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroling.2020.100932. Epub 2020 Aug 4. J Neurolinguistics. 2020. PMID: 33737765 Free PMC article.
-
Do Spanish-English Bilinguals have Their Fingers in Two Pies - or is It Their Toes? An Electrophysiological Investigation of Semantic Access in Bilinguals.Front Psychol. 2012 Feb 2;3:9. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00009. eCollection 2012. Front Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22347197 Free PMC article.
-
Sub-Lexical Processing of Chinese-English Bilinguals: An ERP Analysis.Brain Sci. 2024 Sep 16;14(9):923. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14090923. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39335418 Free PMC article.
-
A Behavioral and Electrophysiological Investigation of the Effect of Bilingualism on Lexical Ambiguity Resolution in Young Adults.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Dec 21;9:682. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00682. eCollection 2015. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26732439 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophysiological cross-language neighborhood density effects in late and early english-welsh bilinguals.Front Psychol. 2012 Oct 18;3:408. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2012.00408. eCollection 2012. Front Psychol. 2012. PMID: 23087661 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

