Tongue acupuncture for the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37304013
- PMCID: PMC10247969
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1124064
Tongue acupuncture for the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objectives: Post-stroke dysphagia is the most common neurological impairment after stroke. The swallowing process is controlled by a network made up of the cerebral cortex, subcortical area, and brainstem structure. The disruption of the swallowing network after stroke leads to dysphagia. The affected swallowing muscles after stroke mainly include the laryngeal muscles (suprahyoid muscle and thyrohyoid muscle) and infrahyoid muscle. These muscles experience kinematic effects and muscle strength weakens, resulting in reduced movement in the swallowing process. Acupuncture can change the excitability of cerebral cortical nerve cells, promote the recovery of neurological function, and enhance neuromuscular excitability, ultimately improving the control of swallowing-related nerves and muscles and promoting swallowing functional recovery. In this meta-analysis, we systematically evaluate the clinical efficacy of acupuncture in the treatment of post-stroke dysphagia.
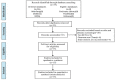
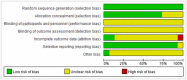
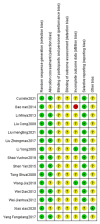
Methods: Randomized controlled trials of tongue acupuncture therapy for post-stroke dysphagia were searched and selected from seven electronic databases (PubMed, CBM, Cochrane, Embase, CNKI, VPCS, and Wan fang). The Cochrane Collaboration tool was used to conduct methodological quality assessment. Rev. Man 5.4 software was utilized to perform data analysis.
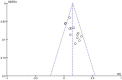
Results: A total of 15 studies with 1,094 patients were included. Meta-analysis Showed that WST score WST score (MD = -0.56, 95% CI (-1.23, 0.12), Z = 1.62, p < 0.00001), SSA score (MD = -1.65, 95% CI (-2.02, -1.28), Z = 8.77, p < 0.00001). These results suggested that the treatment group (tongue acupuncture or tongue acupuncture combined with other therapies) was superior to the control group in reducing WST scores and SSA scores. The clinical efficacy of the tongue acupuncture group was better compared with the control group (MD = 3.83, 95% CI (2.61, 5.62), Z = 6.88, p < 0.00001).
Conclusion: The meta-analysis showed that the total effective rate of patients with dysphagia after stroke in the treatment group (acupuncture, tongue acupuncture, and acupuncture combined with other therapy) was higher than that in the control group. These results indicated that acupuncture, tongue acupuncture, and acupuncture combined with other therapy can improve post-stroke dysphagia.
Keywords: acupuncture therapy; apoplexy; dysphagia after stroke; meta analysis; systematic review; tongue acupuncture.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Xu, Yang, Kuang, Ding, Huang, Guo, Yuan, Xiao, Wang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
[Tongnao Huoluo Liyan acupuncture combined with rehabilitation training for post-stroke dysphagia: a randomized controlled trial].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Apr 12;45(4):435-441. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20240327-k0004. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40229152 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture in aspiration caused by post-stroke dysphagia.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 10;15:1305056. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1305056. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38915795 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture treatment vs. cognitive rehabilitation for post-stroke cognitive impairment: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1035125. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1035125. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36846126 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of acupuncture in Parkinson's disease with dysphagia.Front Neurol. 2023 May 26;14:1099012. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1099012. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37305760 Free PMC article.
-
[Deep acupuncture of Lianquan (CV23) and Yifeng (TE17) in combination with conventional acupuncture of other acupoints is superior to swallowing rehabilitation training in improving post-stroke dysphagia in apoplexy patients].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019 Feb 25;44(2):144-7. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.180018. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2019. PMID: 30945493 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Effect of purpose-directed acupuncture on the pharyngeal phase in stroke patients with dysphagia based on surface electromyography: a randomized controlled trial.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 29;12:1565514. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1565514. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40510853 Free PMC article.
-
Tongue Acupuncture to Treat Dysphagia in Patients with Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Med Acupunct. 2024 Jun 21;36(3):137-145. doi: 10.1089/acu.2023.0073. eCollection 2024 Jun. Med Acupunct. 2024. PMID: 39139365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chinese Expert Consensus Group for Rehabilitation Evaluation and Treatment of Dysphagia (2017). Chinese J. Rehabilitation Med. 39, 881–892. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1424.2017.12.001 - DOI
-
- Cui L. L., Zhang W. D., Wang Y., Jiang L. S., Chen S. F., Liu Y., et al. . (2021). Clinical study on tongue acupuncture combined with swallowing training for dysphagia after stroke. J. Emerg. Tradit. Chin. Med. 30, 312–314. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2021.02.035 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

