Association and mediating mechanism between remnant cholesterol and first-ever stroke among the Chinese general population
- PMID: 37304024
- PMCID: PMC10247974
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1161367
Association and mediating mechanism between remnant cholesterol and first-ever stroke among the Chinese general population
Abstract
Background: Remnant cholesterol (RC) has been suggested to be implicated in atherosclerosis. The objective of the study was to evaluate the association between RC and first-ever stroke in the Chinese general population and to investigate whether the association is mediated via hypertension or diabetes.
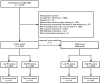
Methods: This study is a retrospective cohort analysis of participants from the China Health and Nutrition Survey. Participants without previous stroke and myocardial infarction in 2009 were enrolled and followed up in 2011 and 2015. Logistic regression analyses were adopted to explore the association of RC with stroke risk. Propensity score methods and doubly robust estimation method were used to ensure the robustness of our findings. Potential mediators were identified by mediation analyses.
Results: A total of 7,035 participants were involved, and during 6 years of follow-up, 78 (1.1%) participants experienced a first-ever stroke. Participants with high RC had a significantly higher incidence of stroke (1.4% versus 0.8%; p = 0.007). High RC was associated with 74% higher stroke risk after adjusting for multiple relevant variables (odds ratio [OR], 1.74; 95% CI, 1.06-2.85). The association was consistent in analyses using propensity score methods and doubly robust estimation method. Hypertension showed a significant mediating effect on the association between RC and stroke, while the mediating effect of diabetes was not significant.
Conclusion: High RC increased the risk of first-ever stroke in the Chinese general population without previous stroke and myocardial infarction, partially through the pathway of hypertension. RC might be a potential target for the primary prevention of stroke.
Keywords: hypertension; mediation analysis; propensity score methods; remnant cholesterol; stroke.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Miao, Chen, Liu, Li and Duan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined and mediating effects of remnant cholesterol and renal function on hypertension risk in Chinese middle-aged and elderly people.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Feb 13;16:1442918. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1442918. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40017692 Free PMC article.
-
Association of remnant cholesterol with hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and their coexistence: the mediating role of inflammation-related indicators.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Sep 26;22(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01915-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 37752554 Free PMC article.
-
Association of remnant cholesterol with chronic kidney disease in middle-aged and elderly Chinese: a population-based study.Acta Diabetol. 2021 Dec;58(12):1615-1625. doi: 10.1007/s00592-021-01765-z. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Acta Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 34181081
-
Investigating the impact of remnant cholesterol on new-onset stroke across diverse inflammation levels: Insights from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS).Int J Cardiol. 2024 Jun 15;405:131946. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2024.131946. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Int J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38460732
-
Remnant cholesterol and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: Metabolism, mechanism, evidence, and treatment.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 17;9:913869. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.913869. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36324753 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of elevated remnant cholesterol on outcomes of acute ischemic stroke patients receiving mechanical thrombectomy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024 Mar;57(3):390-401. doi: 10.1007/s11239-023-02939-y. Epub 2024 Jan 5. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2024. PMID: 38180591
-
Relationship between remnant cholesterol and short-term prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients.Brain Behav. 2024 May;14(5):e3537. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3537. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 38715443 Free PMC article.
-
Remnant cholesterol and the risk of carotid plaque in hypertension: results from a community-based screening among old adults in Hangzhou, China.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 10;14(1):8407. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-58484-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38600230 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Year Changes in Remnant Cholesterol and Stroke Risk in the Chinese Population: A Prospective Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Jun 3;14(11):e038559. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.038559. Epub 2025 May 22. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40401619 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

