Recreational use of oral erectile dysfunction medications among male physicians - A cross-sectional study
- PMID: 37304517
- PMCID: PMC10252768
- DOI: 10.4103/ua.ua_33_22
Recreational use of oral erectile dysfunction medications among male physicians - A cross-sectional study
Abstract
Introduction: Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as the persistent inability to attain and maintain an erection sufficient to permit satisfactory sexual performance. Bypassing health-care providers and obtaining ED medications (EDM) without a prescription are an issue that is faced globally.
Aim: We attempt to assess erectile function (EF) among a local sample of physicians, the psychological effects of recreational EDM use, and compare EF among different user groups.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study done solely on physicians in Saudi Arabia. A self-designed questionnaire including demographics, sexual characteristics, use of ED medication, sexual satisfaction, and the validated international index of EF (IIEF).
Outcome: Physicians misused EDM.
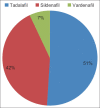
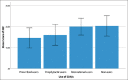
Results: A total of 503 physicians completed the questionnaire. Among participants reporting sexual problems, only 23% received counseling and 3.4% were professionally diagnosed with ED. Among users, 71.2% were using EDM recreationally, 14.4% prophylactically, and 14.4% were prescribed. Participants aged 20-29 IIEF-5 score was significantly lower than participants aged 30-39 years. Prescribed users had a lower IIEF-5 score compared to both recreational users and nonusers.
Clinical implications: Many healthy sexually active men use EDMs recreationally to increase sexual performance.
Strengths and limitations: One of the limitations of our study is that we did not use standardized tools to determine the diagnosis of some important disorders like premature ejaculation. Our study strengths include the very high response rate, with our results truly showing a nationwide self-assessment of sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion: Recreational use of oral EDMs may adversely impact the psychological aspects of sexual function. In our study, physicians misused EDM. We recommend labeling EDMs as restricted medication that requires a prescription to use by a licensed physician.
Keywords: Erectile dysfunction; Saudi Arabia; erectile dysfunction medication; men; phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors; physician; recreational.
Copyright: © 2023 Urology Annals.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA. 1993;270:83–90. - PubMed
-
- Boolell M, Allen MJ, Ballard SA, Gepi-Attee S, Muirhead GJ, Naylor AM, et al. Sildenafil: An orally active type 5 cyclic GMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor for the treatment of penile erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res. 1996;8:47–52. - PubMed
-
- Krenzelok EP. Sildenafil: Clinical toxicology profile. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2000;38:645–51. - PubMed
-
- PDE5 Inhibitor –StatPearls –NCBI Bookshelf. [Last accessed on 2021 Jun 07]. Available form:https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK549843/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources