SLC26 family: a new insight for kidney stone disease
- PMID: 37304821
- PMCID: PMC10247987
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1118342
SLC26 family: a new insight for kidney stone disease
Abstract
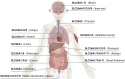
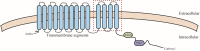
The solute-linked carrier 26 (SLC26) protein family is comprised of multifunctional transporters of substrates that include oxalate, sulphate, and chloride. Disorders of oxalate homeostasis cause hyperoxalemia and hyperoxaluria, leading to urinary calcium oxalate precipitation and urolithogenesis. SLC26 proteins are aberrantly expressed during kidney stone formation, and consequently may present therapeutic targets. SLC26 protein inhibitors are in preclinical development. In this review, we integrate the findings of recent reports with clinical data to highlight the role of SLC26 proteins in oxalate metabolism during urolithogenesis, and discuss limitations of current studies and potential directions for future research.
Keywords: SLC26; hyperoxaluria; kidney stone; oxalate; oxalate metabolism.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Huang, Liu, Liao, Yan and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

