Neutrophil extracellular trap burden correlates with the stenosis of coronary atherosclerosis
- PMID: 37304868
- PMCID: PMC10252804
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15471
Neutrophil extracellular trap burden correlates with the stenosis of coronary atherosclerosis
Abstract
Background: Coronary atherosclerosis diseases (CADs) are associated with chronic inflammation. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are a type of novel proinflammatory cytokines whose levels are dramatically elevated in acute coronary syndrome. We conducted this study to further evaluate the association between circulating NET-associated markers and CAD in Chinese adults.
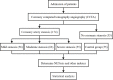
Methods: A total of 174 patients with CAD and 55 healthy controls were screened using percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary computed tomography angiography. Blood lipid levels, blood glucose levels, and blood cell counts were determined using commercial kits. Serum levels of myeloperoxidase (MPO) and neutrophil elastase (NE) were measured using ELISA. Double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in serum was quantified using the Quant-iT PicoGreen assay. We also compared the circulating NET levels with various parameters in the study subjects.
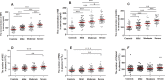
Results: The levels of serum NET markers, dsDNA, MPO, and NE, were significantly elevated in patients with CAD, particularly in the severe group, consistent with the increase in neutrophil counts. The levels of NET markers correlated with the risk factors of AS, increasing with the number of risk factors. NET markers were identified as independent risk factors for severe coronary stenosis and also as predictors of severe CAD.
Conclusion: NETs may be related to AS and serve as indicators or predictors of stenosis in patients with severe CAD.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Coronary heart disease; Myeloperoxidase; Neutrophil elastase; Neutrophil extracellular traps.
©2023 Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
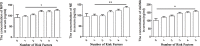

Similar articles
-
NETosis in Long-Term Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Link to Coronary Artery Disease.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 5;12:799539. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.799539. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069582 Free PMC article.
-
Markers of neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with adverse clinical outcome in stable coronary artery disease.Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018 May;25(7):762-769. doi: 10.1177/2047487318760618. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29473463
-
Neutrophil activation and neutrophil derived neutrophil extracellular trap formation in patients with coronary artery ectasia.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020 Mar 2;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01398-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020. PMID: 32122307 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated levels of circulating DNA and chromatin are independently associated with severe coronary atherosclerosis and a prothrombotic state.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Aug;33(8):2032-2040. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301627. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23818485 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in cardiovascular diseases: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic interventions.Kardiol Pol. 2023;81(12):1205-1216. doi: 10.33963/v.kp.98520. Kardiol Pol. 2023. PMID: 38189504 Review.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps in homeostasis and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Sep 20;9(1):235. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01933-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39300084 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid Cells in Myocardial Ischemic Injury: The Role of the Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor.Life (Basel). 2024 Aug 5;14(8):981. doi: 10.3390/life14080981. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The relationship between different exercise conditions and pericoronary inflammation as quantified by coronary CTA in coronary artery disease.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 1;10(3):e25316. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25316. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38352755 Free PMC article.
-
NETosis in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury: From mechanisms to therapies (Review).Biomed Rep. 2025 May 13;23(1):113. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.1991. eCollection 2025 Jul. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 40420974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A comprehensive phenome wide analysis of the role of neutrophils in health and disease.J Leukoc Biol. 2025 Jul 9;117(7):qiaf076. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiaf076. J Leukoc Biol. 2025. PMID: 40435322 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Borissoff JI, Joosen IA, Versteylen MO, Brill A, Fuchs TA, Savchenko AS, Gallant M, Martinod K, Cate HT, Hofstra L, Crijns HJ, Wagner DD, Kietselaer BL. Elevated levels of circulating DNA and chromatin are independently associated with severe coronary atherosclerosis and a prothrombotic state. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2013;33:2032–2040. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301627. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

