Determination of Exogenous Adrenaline Levels in Patients Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
- PMID: 37305245
- PMCID: PMC10249028
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c00555
Determination of Exogenous Adrenaline Levels in Patients Undergoing Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
Abstract
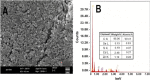
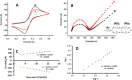
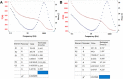
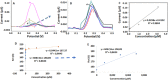
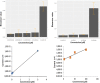
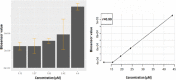
Core-shell quantum dot ZnS/CdSe screen-printed electrodes were used to electrochemically measure human blood plasma levels of exogenous adrenaline administered to cardiac arrest patients. The electrochemical behavior of adrenaline on the modified electrode surface was investigated using differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), cyclic voltammetry, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Under optimal conditions, the linear working ranges of the modified electrode were 0.001-3 μM (DPV) and 0.001-300 μM (EIS). The best limit of detection for this concentration range was 2.79 × 10-8 μM (DPV). The modified electrodes showed good reproducibility, stability, and sensitivity and successfully detected adrenaline levels.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Panchal A. R.; Bartos J. A.; Cabañas J. G.; Kudenchuk P. J.; Kurz M. C.; Lavonas E. J.; Morley P. T.; O’Neil B. J.; Peberdy M. A.; Rittenberger J. C.; Rodriguez A. J.; Sawyer K. N.; Berg K. M. Part 3: Adult Basic and Advanced Life Support: 2020 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care. Circulation 2020, 142, 366–468. 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000916. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim S. H.; Lee J. W.; Yeo I. H. Spectroelectrochemical and electrochemical behavior of epinephrine at a gold electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2000, 45, 2889–2895. 10.1016/s0013-4686(00)00364-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

