Comparative effectiveness of exercise electrocardiography versus exercise echocardiography in women presenting with suspected coronary artery disease: a randomized study
- PMID: 37305342
- PMCID: PMC10253116
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjopen/oead053
Comparative effectiveness of exercise electrocardiography versus exercise echocardiography in women presenting with suspected coronary artery disease: a randomized study
Abstract
Aims: There is a paucity of randomized diagnostic studies in women with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD). This study sought to assess the relative value of exercise stress echocardiography (ESE) compared with exercise electrocardiography (Ex-ECG) in women with CAD.
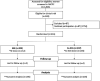
Methods and results: Accordingly, 416 women with no prior CAD and intermediate probability of CAD (mean pre-test probability 41%), were randomized to undergo either Ex-ECG or ESE. The primary endpoints were the positive predictive value (PPV) for the detection of significant CAD and downstream resource utilization. The PPV of ESE and Ex-ECG were 33% and 30% (P = 0.87), respectively for the detection of CAD. There were similar clinic visits (36 vs. 29, P = 0.44) and emergency visits with chest pain (28 vs. 25, P = 0.55) in the Ex-ECG and ESE arms, respectively. At 2.9 years, cardiac events were 6 Ex-ECG vs. 3 ESE, P = 0.31. Although initial diagnosis costs were higher for ESE, more women underwent further CAD testing in the Ex-ECG arm compared to the ESE arm (37 vs. 17, P = 0.003). Overall, there was higher downstream resource utilization (hospital attendances and investigations) in the Ex-ECG arm (P = 0.002). Using National Health Service tariffs 2020/21 (British pounds) the cumulative diagnostic costs were 7.4% lower for Ex-ECG compared with ESE, but this finding is sensitive to the cost differential between ESE and Ex-ECG.
Conclusion: In intermediate-risk women who are able to exercise, Ex-ECG had similar efficacy to an ESE strategy, with higher resource utilization whilst providing cost savings.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Exercise electrocardiography; Randomized study; Stress echocardiography.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



References
-
- Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P, Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M, Nichols M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J 2016;37:3232–3245. - PubMed
-
- Gabet A, Danchin N, Juilliere Y, Olie V. Acute coronary syndrome in women: rising hospitalizations in middle-aged French women, 2004–14. Eur Heart J 2017;38:1060–1065. - PubMed
-
- Bairey Merz CN. Women and ischemic heart disease paradox and pathophysiology. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4:74–77. - PubMed
-
- Scott PE, Unger EF, Jenkins MR, Southworth MR, McDowell TY, Geller RJ, Elahi M, Temple RJ, Woodcock J. Participation of women in clinical trials supporting FDA approval of cardiovascular drugs. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;71:1960–1969. - PubMed
-
- Maron DJ, Hochman JS, Reynolds HR, Bangalore S, O'Brien SM, Boden WE, Chaitman BR, Senior R, López-Sendón J, Alexander KP, Lopes RD, Shaw LJ, Berger JS, Newman JD, Sidhu MS, Goodman SG, Ruzyllo W, Gosselin G, Maggioni AP, White HD, Bhargava B, Min JK, Mancini GBJ, Berman DS, Picard MH, Kwong RY, Ali ZA, Mark DB, Spertus JA, Krishnan MN, Elghamaz A, Moorthy N, Hueb WA, Demkow M, Mavromatis K, Bockeria O, Peteiro J, Miller TD, Szwed H, Doerr R, Keltai M, Selvanayagam JB, Steg PG, Held C, Kohsaka S, Mavromichalis S, Kirby R, Jeffries NO, Harrell FE Jr, Rockhold FW, Broderick S, Ferguson TB Jr, Williams DO, Harrington RA, Stone GW, Rosenberg Y; ISCHEMIA Research Group . Initial invasive or conservative strategy for stable coronary disease. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1395–1407. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

