Current guidelines for diagnosis and management of hepatic involvement in hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia
- PMID: 37305373
- PMCID: PMC10251273
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i5.675
Current guidelines for diagnosis and management of hepatic involvement in hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia
Abstract
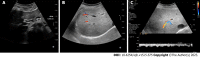
Hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia (HHT), also known as Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome, is the most common cause of hepatic vascular malformations in adults. Different vascular shunts (arteriovenous, arterioportal or portovenous) lead to different clinical manifestations. Even though no hepatic-related symptoms are reported in the majority of cases, the severity of liver disease could lead to refractory medical conditions, in some cases requiring liver transplantation. The aim of this manuscript is to provide an updated overview of the current evidence regarding the diagnosis and treatment of HHT liver involvement and liver-related complications.
Keywords: Hepatic vascular malformations; Hereditary hemorrhagic teleangiectasia; Liver; Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Shovlin CL, Guttmacher AE, Buscarini E, Faughnan ME, Hyland RH, Westermann CJ, Kjeldsen AD, Plauchu H. Diagnostic criteria for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu-Osler-Weber syndrome) Am J Med Genet . 2000;91:66–67. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

