Therapeutic effects of phlorotannins in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders
- PMID: 37305552
- PMCID: PMC10249478
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1193590
Therapeutic effects of phlorotannins in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders
Abstract
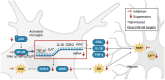
Phlorotannins are natural polyphenolic compounds produced by brown marine algae and are currently found in nutritional supplements. Although they are known to cross the blood-brain barrier, their neuropharmacological actions remain unclear. Here we review the potential therapeutic benefits of phlorotannins in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In mouse models of Alzheimer's disease, ethanol intoxication and fear stress, the phlorotannin monomer phloroglucinol and the compounds eckol, dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol A have been shown to improve cognitive function. In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, phloroglucinol treatment led to improved motor performance. Additional neurological benefits associated with phlorotannin intake have been demonstrated in stroke, sleep disorders, and pain response. These effects may stem from the inhibition of disease-inducing plaque synthesis and aggregation, suppression of microglial activation, modulation of pro-inflammatory signaling, reduction of glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, and scavenging of reactive oxygen species. Clinical trials of phlorotannins have not reported significant adverse effects, suggesting these compounds to be promising bioactive agents in the treatment of neurological diseases. We therefore propose a putative biophysical mechanism of phlorotannin action in addition to future directions for phlorotannin research.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; neurodegenerative disease; phlorotannin; polyphenol.
Copyright © 2023 Kwon, Kwon, Hwang, Shin and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
YJK was previously employed, and OIK is currently employed by Botamedi Brain Health and Medical Care Company Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Ahn G. N., Kim K. N., Cha S. H., Song C.-B., Lee J., Heo M.-S., et al. . (2006). Antioxidant activities of phlorotannins purified from Ecklonia cava on free radical scavenging using ESR and H2O2-mediated DNA damage. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 226, 71–79. doi: 10.1007/s00217-006-0510-y - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

