Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella pertussis: Similarities and Differences in Infection, Immuno-Modulation, and Vaccine Considerations
- PMID: 37306571
- PMCID: PMC10512794
- DOI: 10.1128/cmr.00164-22
Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella pertussis: Similarities and Differences in Infection, Immuno-Modulation, and Vaccine Considerations
Abstract
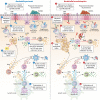
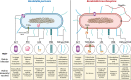
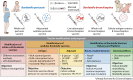
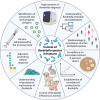
Bordetella pertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica belong to the genus Bordetella, which comprises 14 other species. B. pertussis is responsible for whooping cough in humans, a severe infection in children and less severe or chronic in adults. These infections are restricted to humans and currently increasing worldwide. B. bronchiseptica is involved in diverse respiratory infections in a wide range of mammals. For instance, the canine infectious respiratory disease complex (CIRDC), characterized by a chronic cough in dogs. At the same time, it is increasingly implicated in human infections, while remaining an important pathogen in the veterinary field. Both Bordetella can evade and modulate host immune responses to support their persistence, although it is more pronounced in B. bronchiseptica infection. The protective immune responses elicited by both pathogens are comparable, while there are important characteristics in the mechanisms that differ. However, B. pertussis pathogenesis is more difficult to decipher in animal models than those of B. bronchiseptica because of its restriction to humans. Nevertheless, the licensed vaccines for each Bordetella are different in terms of formulation, route of administration and immune responses induced, with no known cross-reaction between them. Moreover, the target of the mucosal tissues and the induction of long-lasting cellular and humoral responses are required to control and eliminate Bordetella. In addition, the interaction between both veterinary and human fields are essential for the control of this genus, by preventing the infections in animals and the subsequent zoonotic transmission to humans.
Keywords: Bordetella; Bordetella bronchiseptica; Bordetella pertussis; adjuvants; immunization; infectious disease; mucosal immunity; one health; persistence; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Parkhill J, Sebaihia M, Preston A, Murphy LD, Thomson N, Harris DE, Holden MTG, Churcher CM, Bentley SD, Mungall KL, Cerdeño-Tárraga AM, Temple L, James K, Harris B, Quail MA, Achtman M, Atkin R, Baker S, Basham D, Bason N, Cherevach I, Chillingworth T, Collins M, Cronin A, Davis P, Doggett J, Feltwell T, Goble A, Hamlin N, Hauser H, Holroyd S, Jagels K, Leather S, Moule S, Norberczak H, O'Neil S, Ormond D, Price C, Rabbinowitsch E, Rutter S, Sanders M, Saunders D, Seeger K, Sharp S, Simmonds M, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Stevens K, Unwin L, et al. 2003. Comparative analysis of the genome sequences of Bordetella pertussis, Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica. Nat Genet 35:32–40. doi:10.1038/ng1227. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

