Syk Inhibition Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Overcomes Gemcitabine-Induced Immunosuppression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 37306759
- PMCID: PMC10416758
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-3645
Syk Inhibition Reprograms Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Overcomes Gemcitabine-Induced Immunosuppression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
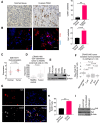
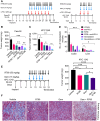
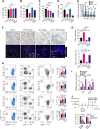
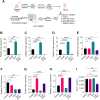
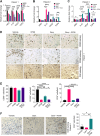
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an insidious disease with a low 5-year survival rate. PDAC is characterized by infiltration of abundant tumor-associated macrophages (TAM), which promote immune tolerance and immunotherapeutic resistance. Here we report that macrophage spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) promotes PDAC growth and metastasis. In orthotopic PDAC mouse models, genetic deletion of myeloid Syk reprogrammed macrophages into immunostimulatory phenotype, increased the infiltration, proliferation, and cytotoxicity of CD8+ T cells, and repressed PDAC growth and metastasis. Furthermore, gemcitabine (Gem) treatment induced an immunosuppressive microenvironment in PDAC by promoting protumorigenic polarization of macrophages. In contrast, treatment with the FDA-approved Syk inhibitor R788 (fostamatinib) remodeled the tumor immune microenvironment, "re-educated" protumorigenic macrophages towards an immunostimulatory phenotype and boosted CD8+ T-cell responses in Gem-treated PDAC in orthotopic mouse models and an ex vivo human pancreatic slice culture model. These findings illustrate the potential of Syk inhibition for enhancing the antitumor immune responses in PDAC and support the clinical evaluation of R788 either alone or together with Gem as a potential treatment strategy for PDAC.
Significance: Syk blockade induces macrophage polarization to an immunostimulatory phenotype, which enhances CD8+ T-cell responses and improves gemcitabine efficacy in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, a clinically challenging malignancy.
©2023 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS122835/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA248457/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K22 CA229594/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA226803/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA109467/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121941/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA217885/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA176058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA220341/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA247551/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154480/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE026870/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

