Automated full body tumor segmentation in DOTATATE PET/CT for neuroendocrine cancer patients
- PMID: 37306856
- PMCID: PMC10980256
- DOI: 10.1007/s11548-023-02968-1
Automated full body tumor segmentation in DOTATATE PET/CT for neuroendocrine cancer patients
Abstract
Purpose: Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a rare form of cancer that can occur anywhere in the body and commonly metastasizes. The large variance in location and aggressiveness of the tumors makes it a difficult cancer to treat. Assessments of the whole-body tumor burden in a patient image allow for better tracking of disease progression and inform better treatment decisions. Currently, radiologists rely on qualitative assessments of this metric since manual segmentation is unfeasible within a typical busy clinical workflow.
Methods: We address these challenges by extending the application of the nnU-net pipeline to produce automatic NET segmentation models. We utilize the ideal imaging type of 68Ga-DOTATATE PET/CT to produce segmentation masks from which to calculate total tumor burden metrics. We provide a human-level baseline for the task and perform ablation experiments of model inputs, architectures, and loss functions.
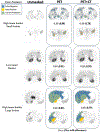
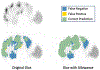
Results: Our dataset is comprised of 915 PET/CT scans and is divided into a held-out test set (87 cases) and 5 training subsets to perform cross-validation. The proposed models achieve test Dice scores of 0.644, on par with our inter-annotator Dice score on a subset 6 patients of 0.682. If we apply our modified Dice score to the predictions, the test performance reaches a score of 0.80.
Conclusion: In this paper, we demonstrate the ability to automatically generate accurate NET segmentation masks given PET images through supervised learning. We publish the model for extended use and to support the treatment planning of this rare cancer.
Keywords: Automatic segmentation; DOTATATE; Neuroendocrine tumor; PET; Radiology; Tumor burden; nnUnet.
© 2023. CARS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Fallahi B, Manafi-Farid R, Eftekhari M, Fard-Esfahani A, EmamiAderkani A, Geramifar P, Akhlaghi M, Taheri APH, and Beiki D. Diagnostic efficiency of 68ga-dotatate pet/ct as compared to 99mtc-octreotide spect/ct and conventional morphologic modalities in neuroendocrine tumors. Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol., 7:129–140, 2019. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonelli M, Reinkeb A, Bakase S, Farahanif K, Kopp-Schneiderg A, Landman BA, Litjens G, Menze B, Ronneberger O, Summers RM, Van Ginneken B, Bilello M, Bilic P, Christ PF, Do RKG, Gollub MJ, Heckers SH, Huisman H, Jarnagin WR, McHugo MK, Napel S, Pernicka JSG, Rohde K, Tonbo-Gomex C, Vorontsov E, Huisman H, Meakin JA, Ourselin S, Wiesenfarth M, Arbelaex P, Bae B, Chen S, Daza L, Feng J, He B, Isensee F, Ji Y, Jia F, Kim N, Kim I, Merhof D, Pai A, Park B, Perslev M, Rezaiifar R, Rippel O, Sarasua I, Shen W, Son J, Wachinger C, Wang L, Wang Y, Xia Y, Xu. D, Xu Z, Zheng Y, Simpson AL, Maier-Hein L, and Jorge Cardoso M. The medical segmentation decathlon. Nature Digital Medicine, 2021. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

