Hemostatic biomarkers associated with postpartum hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 37307172
- PMCID: PMC10562765
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2023010143
Hemostatic biomarkers associated with postpartum hemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
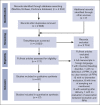
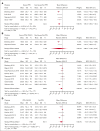
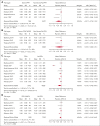
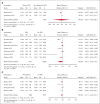
Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is a leading cause of maternal morbi-mortality. Although obstetric risk factors are well described, the impact of predelivery hematologic and hemostatic biomarkers remains incompletely understood. In this systematic review, we aimed to summarize the available literature on the association between predelivery hemostatic biomarkers and PPH/severe PPH. Searching MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CENTRAL databases from inception to October 2022, we included observational studies on unselected pregnant women without bleeding disorder reporting on PPH and on predelivery hemostatic biomarkers. Two review authors independently performed title, abstract and full-text screening, upon which quantitative syntheses of studies reporting on the same hemostatic biomarker were conducted, calculating the mean difference (MD) between women with PPH/severe PPH and controls. A search on 18 October 2022 yielded 81 articles fitting our inclusion criteria. The heterogeneity between studies was considerable. With regard to PPH, the estimated average MD in the investigated biomarkers (platelets, fibrinogen, hemoglobin, Ddimer, activated partial thromboplastin time, and prothrombin time) were not statistically significant. Women who developed severe PPH had lower predelivery platelets than controls (MD = -26.0 109/L; 95% confidence interval, -35.8 to -16.1), whereas differences in predelivery fibrinogen concentration (MD = -0.31 g/L; 95% confidence interval, -0.75 to 0.13) and levels of factor XIII or hemoglobin were not statistically significant in women with and without severe PPH. Predelivery platelet counts were, on average, lower in women with severe PPH compared with controls, suggesting the potential usefulness of this biomarker for predicting severe PPH. This trial was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews as CRD42022368075.
© 2023 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The permanent affiliation for C.d.M. is Internal Medicine, Vascular Medicine and Pneumology Department, UMR 1304, GETBO, UBO, Brest University Hospital, Brest, France.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez-Brown V, Schneider P. Prevention of postpartum hemorrhage. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;25(5) - PubMed
-
- Lautredou M, Pan-Petesch B, Dupré PF, et al. Excessive gestational weight gain is an independent risk factor for gestational diabetes mellitus in singleton pregnancies: results from a French cohort study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2022;275:31–36. - PubMed
-
- Neary C, Naheed S, McLernon DJ, Black M. Predicting risk of postpartum haemorrhage: a systematic review. BJOG An Int J Obstet Gynaecol. 2021;128(1):46–53. - PubMed

