Cross talk between Paneth and tuft cells drives dysbiosis and inflammation in the gut mucosa
- PMID: 37307458
- PMCID: PMC10288547
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2219431120
Cross talk between Paneth and tuft cells drives dysbiosis and inflammation in the gut mucosa
Abstract
Gut microbiota imbalance (dysbiosis) is increasingly associated with pathological conditions, both within and outside the gastrointestinal tract. Intestinal Paneth cells are considered to be guardians of the gut microbiota, but the events linking Paneth cell dysfunction with dysbiosis remain unclear. We report a three-step mechanism for dysbiosis initiation. Initial alterations in Paneth cells, as frequently observed in obese and inflammatorybowel diseases patients, cause a mild remodeling of microbiota, with amplification of succinate-producing species. SucnR1-dependent activation of epithelial tuft cells triggers a type 2 immune response that, in turn, aggravates the Paneth cell defaults, promoting dysbiosis and chronic inflammation. We thus reveal a function of tuft cells in promoting dysbiosis following Paneth cell deficiency and an unappreciated essential role of Paneth cells in maintaining a balanced microbiota to prevent inappropriate activation of tuft cells and deleterious dysbiosis. This succinate-tuft cell inflammation circuit may also contribute to the chronic dysbiosis observed in patients.
Keywords: Paneth cells; antimicrobial peptides; gut inflammation; microbiota dysbiosis; tuft cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
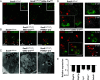
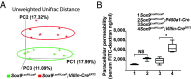
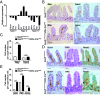

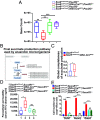


References
-
- Kundu P., Blacher E., Elinav E., Pettersson S., Our gut microbiome: The evolving inner self. Cell 171, 1481–1493 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Turnbaugh P. J., et al. , An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444, 1027–1031 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Järbrink-Sehgal E., Andreasson A., The gut microbiota and mental health in adults. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 62, 102–114 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Settanni C. R., Ianiro G., Bibbò S., Cammarota G., Gasbarrini A., Gut microbiota alteration and modulation in psychiatric disorders: Current evidence on fecal microbiota transplantation. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 109, 110258 (2021). - PubMed

