Improving community health worker treatment for malaria, diarrhoea, and pneumonia in Uganda through inSCALE community and mHealth innovations: A cluster randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 37307519
- PMCID: PMC10260253
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000217
Improving community health worker treatment for malaria, diarrhoea, and pneumonia in Uganda through inSCALE community and mHealth innovations: A cluster randomised controlled trial
Abstract
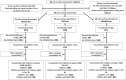
The inSCALE cluster randomised controlled trial in Uganda evaluated two interventions, mHealth and Village Health Clubs (VHCs) which aimed to improve Community Health Worker (CHW) treatment for malaria, diarrhoea, and pneumonia within the national Integrated Community Case Management (iCCM) programme. The interventions were compared with standard care in a control arm. In a cluster randomised trial, 39 sub-counties in Midwest Uganda, covering 3167 CHWs, were randomly allocated to mHealth; VHC or usual care (control) arms. Household surveys captured parent-reported child illness, care seeking and treatment practices. Intention-to-treat analysis estimated the proportion of appropriately treated children with malaria, diarrhoea, and pneumonia according to WHO informed national guidelines. The trial was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01972321). Between April-June 2014, 7679 households were surveyed; 2806 children were found with malaria, diarrhoea, or pneumonia symptoms in the last one month. Appropriate treatment was 11% higher in the mHealth compared to the control arm (risk ratio [RR] 1.11, 95% CI 1.02, 1.21; p = 0.018). The largest effect was on appropriate treatment for diarrhoea (RR 1.39; 95% CI 0.90, 2.15; p = 0.134). The VHC intervention increased appropriate treatment by 9% (RR 1.09; 95% CI 1.01, 1.18; p = 0.059), again with largest effect on treatment of diarrhoea (RR 1.56, 95% CI 1.04, 2.34, p = 0.030). CHWs provided the highest levels of appropriate treatment compared to other providers. However, improvements in appropriate treatment were observed at health facilities and pharmacies, with CHW appropriate treatment the same across the arms. The rate of CHW attrition in both intervention arms was less than half that of the control arm; adjusted risk difference mHealth arm -4.42% (95% CI -8.54, -0.29, p = 0.037) and VHC arm -4.75% (95% CI -8.74, -0.76, p = 0.021). Appropriate treatment by CHWs was encouragingly high across arms. The inSCALE mHealth and VHC interventions have the potential to reduce CHW attrition and improve the care quality for sick children, but not through improved CHW management as we had hypothesised. Trial Registration:ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT01972321).
Copyright: © 2023 Källander et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- You D, Hug L, Ejdemyr S, Idele P, Hogan D, Mathers C, et al.. Global, regional, and national levels and trends in under-5 mortality between 1990 and 2015, with scenario-based projections to 2030: a systematic analysis by the UN Inter-agency Group for Child Mortality Estimation. Lancet. 2015;386(10010):2275–86. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00120-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Roberton T, Carter ED, Chou VB, Stegmuller AR, Jackson BD, Tam Y, et al.. Early estimates of the indirect effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal and child mortality in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2020;8(7):e901–e8. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30229-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Young M, Wolfheim C, Marsh DR, Hammamy D. World Health Organization/United Nations Children’s Fund joint statement on integrated community case management: an equity-focused strategy to improve access to essential treatment services for children. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012;87(5 Suppl):6–10. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.12-0221 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hazel E, Bryce J, The IIP-JHU iCCM Evaluation Working Group. On Bathwater, Babies, and Designing Programs for Impact: Evaluations of the Integrated Community Case Management Strategy in Burkina Faso, Ethiopia, and Malawi. The American journal of tropical medicine and hygiene. 2016;94(3):568–70. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.94-3intro1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous