Sensitivity to Neutralizing Antibodies and Resistance to Type I Interferons in SARS-CoV-2 R.1 Lineage Variants, Canada
- PMID: 37308158
- PMCID: PMC10310370
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2907.230198
Sensitivity to Neutralizing Antibodies and Resistance to Type I Interferons in SARS-CoV-2 R.1 Lineage Variants, Canada
Abstract
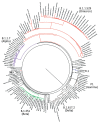
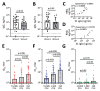
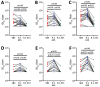
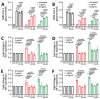
Isolating and characterizing emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants is key to understanding virus pathogenesis. In this study, we isolated samples of the SARS-CoV-2 R.1 lineage, categorized as a variant under monitoring by the World Health Organization, and evaluated their sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies and type I interferons. We used convalescent serum samples from persons in Canada infected either with ancestral virus (wave 1) or the B.1.1.7 (Alpha) variant of concern (wave 3) for testing neutralization sensitivity. The R.1 isolates were potently neutralized by both the wave 1 and wave 3 convalescent serum samples, unlike the B.1.351 (Beta) variant of concern. Of note, the R.1 variant was significantly more resistant to type I interferons (IFN-α/β) than was the ancestral isolate. Our study demonstrates that the R.1 variant retained sensitivity to neutralizing antibodies but evolved resistance to type I interferons. This critical driving force will influence the trajectory of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Canada; N501Y spike; SARS-CoV-2; VoC; VuM; coronavirus disease; neutralizing antibodies; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; type I interferons; variant under monitoring; variants of concern; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity of convalescent and vaccinated sera against clinical isolates of ancestral SARS-CoV-2, Beta, Delta, and Omicron variants.Med. 2022 Jun 10;3(6):422-432.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2022.04.002. Epub 2022 Apr 14. Med. 2022. PMID: 35437520 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of spike N501Y mutation on neutralizing activity and RBD binding of SARS-CoV-2 convalescent serum.EBioMedicine. 2021 Sep;71:103544. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103544. Epub 2021 Aug 19. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34419925 Free PMC article.
-
The P681H Mutation in the Spike Glycoprotein of the Alpha Variant of SARS-CoV-2 Escapes IFITM Restriction and Is Necessary for Type I Interferon Resistance.J Virol. 2022 Dec 14;96(23):e0125022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01250-22. Epub 2022 Nov 9. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 36350154 Free PMC article.
-
Human Genomics of COVID-19 Pneumonia: Contributions of Rare and Common Variants.Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023 Aug 10;6:465-486. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biodatasci-020222-021705. Epub 2023 May 17. Annu Rev Biomed Data Sci. 2023. PMID: 37196358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type I interferon pathway genetic variants in severe COVID-19.Virus Res. 2024 Apr;342:199339. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2024.199339. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Virus Res. 2024. PMID: 38354910 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 nsp15 endoribonuclease antagonizes dsRNA-induced antiviral signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Apr 9;121(15):e2320194121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320194121. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38568967 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tuite AR, Fisman DN, Odutayo A, Bobos P, Allen V, Bogoch II, et al. COVID-19 hospitalizations, ICU admissions and deaths associated with the new variants of concern. Science Briefs of the Ontario COVID-19 Science Advisory Table. 2021. Mar 29 [cited 2023 Feb 1]. https://covid19-sciencetable.ca/sciencebrief/covid-19-hospitalizations-i...
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

