Safety profile of upadacitinib in patients at risk of cardiovascular disease: integrated post hoc analysis of the SELECT phase III rheumatoid arthritis clinical programme
- PMID: 37308218
- PMCID: PMC10423494
- DOI: 10.1136/ard-2023-223916
Safety profile of upadacitinib in patients at risk of cardiovascular disease: integrated post hoc analysis of the SELECT phase III rheumatoid arthritis clinical programme
Abstract
Objective: Increased risk of serious adverse events (AEs) was reported for tofacitinib relative to tumour necrosis factor inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) aged ≥50 years enriched for cardiovascular (CV) risk (ORAL Surveillance). We assessed post hoc the potential risk of upadacitinib in a similar RA population.
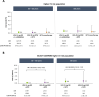
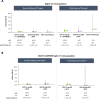
Methods: Pooled safety data from six phase III trials were evaluated post hoc for AEs in patients receiving upadacitinib 15 mg once a day (with or without conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs), adalimumab 40 mg every other week with concomitant methotrexate (MTX), or MTX monotherapy in the overall trial population and in a subset of patients with higher CV risk (aged ≥50 years, ≥1 CV risk factor). Higher-risk patients from a head-to-head study of upadacitinib 15 mg versus adalimumab (SELECT-COMPARE) were assessed in parallel. Exposure-adjusted incidence rates for treatment-emergent AEs were summarised based on exposure to upadacitinib or comparators.
Results: A total of 3209 patients received upadacitinib 15 mg, 579 received adalimumab and 314 received MTX monotherapy; ~54% of the patients were included in the overall and SELECT-COMPARE higher-risk populations. Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), malignancy (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer (NMSC)) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) were more frequent in the higher-risk cohorts versus the overall population but were generally similar across treatment groups. Rates of serious infections in higher-risk populations and herpes zoster (HZ) and NMSC in all populations were higher with upadacitinib 15 mg than comparators.
Conclusions: An increased risk of MACE, malignancy (excluding NMSC) and VTE was observed in higher-risk populations with RA, yet risk was comparable between upadacitinib-treated and adalimumab-treated patients. Higher rates of NMSC and HZ were observed with upadacitinib versus comparators across all populations, and increased rates of serious infections were detected in upadacitinib-treated patients at higher CV risk.
Trial registration numbers: NCT02706873, NCT02675426, NCT02629159, NCT02706951, NCT02706847 and NCT03086343.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis; cardiovascular diseases; methotrexate; tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: RF: research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, AstraZeneca, Biogen, BMS, Boehringer-Ingleheim, Flexion, Galapagos, Galvani, Genentech, Gilead, GSK, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB. JRC: consulting fees and research support from AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, CorEvitas, Lilly, Novartis, Myriad, Sanofi, Pfizer and UCB. CC-S: research grants from AbbVie, BMS, CSL Behring and Pfizer; consultancy for AbbVie, Priovant Therapeutics, Octapharma, BMS, Pfizer, Gilead and Regeneron-Sanofi. EFM: research grants and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Novartis, Lilly, Pfizer, Roche, BMS, Sandoz, GSK, Janssen and Sanofi. KY: consultancy fees from AbbVie, Pfizer, Gilead G.K., Asahi Kasei Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Eli Lilly Japan and Japan Tobacco; member of the speaker’s bureau at Astellas, Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, Eisai, Eli Lilly Japan, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma, Pfizer and Takeda; and research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Chugai, GlaxoSmithKline and Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma. CR: consultancy and speaking fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Roche, BMS, Galapagos, GSK, Lilly, Hospira, Biogen, Sandoz, Mylan, Novartis and Pfizer. GRB: speaking or consulting fees from AbbVie, BMS, Lilly, Galapagos, Janssen, MSD, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi and UCB. JL, HP, DD and SS: AbbVie employees and may own stocks or options.
Figures





References
-
- US Food and Drug Administration . FDA requires warnings about increased risk of serious heart-related events, cancer, blood clots, and death for JAK inhibitors that treat certain chronic inflammatory conditions. 2021. Available: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-safety-and-availability/fda-requires-warn... [Accessed 19 Dec 2022].

