Safety and incremental prognostic value of stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients with known chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 37308923
- PMCID: PMC10259036
- DOI: 10.1186/s12968-023-00939-8
Safety and incremental prognostic value of stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients with known chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the main cause of mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD). Although several studies have demonstrated the consistently high prognostic value of stress cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR), its prognostic value in patients with CKD is not well established. We aimed to assess the safety and the incremental prognostic value of vasodilator stress perfusion CMR in consecutive symptomatic patients with known CKD.
Methods: Between 2008 and 2021, we conducted a retrospective dual center study with all consecutive symptomatic patients with known stage 3 CKD, defined by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) between 30 and 60 ml/min/1.73 m2, referred for vasodilator stress CMR. All patients with eGFR < 30 ml/min/1.73 m2 (n = 62) were excluded due the risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. All patients were followed for the occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) defined as cardiac death or recurrent nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI). Cox regression analysis was used to determine the prognostic value of stress CMR parameters.
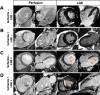
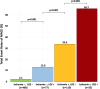
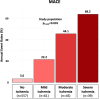
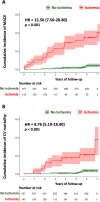
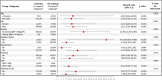
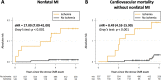
Results: Of 825 patients with known CKD (71.4 ± 8.8 years, 70% men), 769 (93%) completed the CMR protocol. Follow-up was available in 702 (91%) (median follow-up 6.4 (4.0-8.2) years). Stress CMR was well tolerated without occurrence of death or severe adverse event related to the injection of gadolinium or cases of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. The presence of inducible ischemia was associated with the occurrence of MACE (hazard ratio [HR] 12.50; 95% confidence interval [CI] 7.50-20.8; p < 0.001). In multivariable analysis, ischemia and late gadolinium enhancement were independent predictors of MACE (HR 15.5; 95% CI 7.72 to 30.9; and HR 4.67 [95% CI 2.83-7.68]; respectively, both p < 0.001). After adjustment, stress CMR findings showed the best improvement in model discrimination and reclassification above traditional risk factors (C-statistic improvement: 0.13; NRI = 0.477; IDI = 0.049).
Conclusions: In patients with known stage 3 CKD, stress CMR is safe and its findings have an incremental prognostic value to predict MACE over traditional risk factors.
Keywords: Cardiovascular events; Cardiovascular magnetic resonance; Chronic kidney disease; Myocardial ischemia; Prognosis; Stress testing; Unrecognized myocardial infarction.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Solenn Toupin is an employee of Siemens Healthcare. Other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of vasodilator stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance after inconclusive stress testing.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 Jul 5;23(1):89. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00785-6. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 34218805 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Value of Vasodilator Stress Perfusion Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Patients With Prior Myocardial Infarction.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021 Nov;14(11):2138-2151. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2021.04.021. Epub 2021 Jun 16. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34147458
-
Long-term prognostic value of stress perfusion cardiovascular magnetic resonance in patients without known coronary artery disease.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 Apr 8;23(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00737-0. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 33827603 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of stress cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with known or suspected coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Aug 27;62(9):826-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.03.080. Epub 2013 May 30. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23727209 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of myocardial salvage index by cardiac magnetic resonance in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2023 Nov;33(11):8214-8225. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09739-1. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37328640
Cited by
-
Prognostic significance of dobutamine stress echocardiography in patients with chronic kidney disease and known or suspected coronary artery disease: a 5-year follow-up study.Heart Vessels. 2025 Mar;40(3):210-218. doi: 10.1007/s00380-024-02464-9. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Heart Vessels. 2025. PMID: 39311944
-
Feasibility and Prognostic Value of Stress Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Patients With End-Stage Renal Disease.JACC Adv. 2025 Jul 28;4(8):102008. doi: 10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.102008. Online ahead of print. JACC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40730050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohtake T, Kobayashi S, Moriya H, Negishi K, Okamoto K, Maesato K, et al. High prevalence of occult coronary artery stenosis in patients with chronic kidney disease at the initiation of renal replacement therapy: an angiographic examination. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16:1141–1148. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004090765. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

