Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) attenuates tacrolimus-induced hepatic lipid accumulation through transcription factor EB (TFEB)-regulated lipophagy
- PMID: 37309040
- PMCID: PMC10264170
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B2200562
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) attenuates tacrolimus-induced hepatic lipid accumulation through transcription factor EB (TFEB)-regulated lipophagy
Abstract
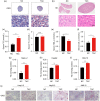
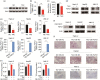
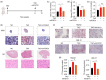
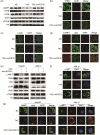
Tacrolimus (TAC), also called FK506, is one of the classical immunosuppressants to prevent allograft rejection after liver transplantation. However, it has been proved to be associated with post-transplant hyperlipemia. The mechanism behind this is unknown, and it is urgent to explore preventive strategies for hyperlipemia after transplantation. Therefore, we established a hyperlipemia mouse model to investigate the mechanism, by injecting TAC intraperitoneally for eight weeks. After TAC treatment, the mice developed hyperlipemia (manifested as elevated triglyceride (TG) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), as well as decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c)). Accumulation of lipid droplets was observed in the liver. In addition to lipid accumulation, TAC induced inhibition of the autophagy-lysosome pathway (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3β (LC3B) II/I and LC3B II/actin ratios, transcription factor EB (TFEB), protein 62 (P62), and lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1)) and downregulation of fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) in vivo. Overexpression of FGF21 may reverse TAC-induced TG accumulation. In this mouse model, the recombinant FGF21 protein ameliorated hepatic lipid accumulation and hyperlipemia through repair of the autophagy-lysosome pathway. We conclude that TAC downregulates FGF21 and thus exacerbates lipid accumulation by impairing the autophagy-lysosome pathway. Recombinant FGF21 protein treatment could therefore reverse TAC-caused lipid accumulation and hypertriglyceridemia by enhancing autophagy.
他克莫司(TAC),也称为FK506,是预防肝移植后同种异体移植排斥反应的经典免疫抑制剂之一。然而,它已被证明与移植后高脂血症有关。但其背后的机制尚不清楚,因此迫切需要探索移植后高脂血症的预防策略。我们通过腹腔注射8周TAC建立了一个高脂血症小鼠模型来研究其机制。TAC处理后,小鼠发生高脂血症(表现为甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)升高,以及高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)降低)以及肝脏脂质的累积。除脂质积累外,TAC还抑制了自噬-溶酶体途径(LC3B II/I和LC3BII/actin比值、转录因子EB(TFEB)、P62和LAMP1),并下调成纤维细胞生长因子21(FGF21)的表达。而FGF21的过表达可逆转TAC诱导的TG积累。在该小鼠模型中,重组FGF21蛋白通过修复自噬-溶酶体途径改善肝脏脂质积累和高脂血症。综上所述,TAC下调FGF21,从而通过抑制自噬-溶酶体途径来加剧脂质积累。此外,重组FGF21蛋白处理可以通过增强自噬来逆转TAC引起的脂质积累和高甘油三酯血症。.
他克莫司(TAC),也称为FK506,是预防肝移植后同种异体移植排斥反应的经典免疫抑制剂之一。然而,它已被证明与移植后高脂血症有关。但其背后的机制尚不清楚,因此迫切需要探索移植后高脂血症的预防策略。我们通过腹腔注射8周TAC建立了一个高脂血症小鼠模型来研究其机制。TAC处理后,小鼠发生高脂血症(表现为甘油三酯(TG)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-c)升高,以及高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(HDL-c)降低)以及肝脏脂质的累积。除脂质积累外,TAC还抑制了自噬-溶酶体途径(LC3B II/I和LC3BII/actin比值、转录因子EB(TFEB)、P62和LAMP1),并下调成纤维细胞生长因子21(FGF21)的表达。而FGF21的过表达可逆转TAC诱导的TG积累。在该小鼠模型中,重组FGF21蛋白通过修复自噬-溶酶体途径改善肝脏脂质积累和高脂血症。综上所述,TAC下调FGF21,从而通过抑制自噬-溶酶体途径来加剧脂质积累。此外,重组FGF21蛋白处理可以通过增强自噬来逆转TAC引起的脂质积累和高甘油三酯血症。
Keywords: Autophagy; Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21); Lipid; Lipophagy; Lysosome; Tacrolimus; Transcription factor EB (TFEB).
Figures

Similar articles
-
The ménage à trois of autophagy, lipid droplets and liver disease.Autophagy. 2022 Jan;18(1):50-72. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1895658. Epub 2021 Apr 2. Autophagy. 2022. PMID: 33794741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Formononetin alleviates hepatic steatosis by facilitating TFEB-mediated lysosome biogenesis and lipophagy.J Nutr Biochem. 2019 Nov;73:108214. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.07.005. Epub 2019 Jul 25. J Nutr Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31520816
-
Liraglutide Alleviates Hepatic Steatosis by Activating the TFEB-Regulated Autophagy-Lysosomal Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 27;8:602574. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.602574. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33330497 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factor EB inhibits non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through fibroblast growth factor 21.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Nov;100(11):1587-1597. doi: 10.1007/s00109-022-02256-6. Epub 2022 Sep 14. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36102936
-
FGF21-mediated autophagy: Remodeling the homeostasis in response to stress in liver diseases.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 13;11(3):101027. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.05.019. eCollection 2024 May. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38292187 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of tacrolimus-related genes in familial combined hyperlipidemia and development of a diagnostic model using bioinformatics analysis.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 19;11(3):e41705. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41705. eCollection 2025 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39916852 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of immunosuppressants on tumor pulmonary metastasis: new insight into transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Biol Med. 2024 Dec 24;21(11):1033-49. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2024.0267. Cancer Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 39718153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFA1100500/the National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 92159202, 81930016 and 82102910/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2019C03050/the Key Research & Development Plan of Zhejiang Province
- OO20200093/the Construction Fund of Key Medical Disciplines of Hangzhou
- 2020M671762/the Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

