Major mixed motility disorders: An important subset of esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction
- PMID: 37309619
- PMCID: PMC10266834
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.14555
Major mixed motility disorders: An important subset of esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction
Abstract
Background: Esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction (EGJOO) is an esophageal motility disorder characterized by a lack of relaxation of the esophagogastric junction (EGJ), with preserved esophageal body peristalsis. We propose new terminology for the coexistence of EGJOO with hypercontractile esophagus and distal esophageal spasm as a major mixed motility disorder (MMMD), and normal peristalsis or a minor disorder of peristalsis such as ineffective esophageal motility with EGJOO as isolated or ineffective EGJOO (IEGJOO).
Methods: We reviewed prior diagnoses of EGJOO, stratified diagnoses as IEGJOO or MMMD, and compared their symptomatic presentations, high-resolution manometry (HRM) and endoluminal functional lumen imaging probe (EndoFLIP) metrics, and treatment responses at 2-6 months of follow-up.
Results: Out of a total of 821 patients, 142 met CCv3 criteria for EGJOO. Twenty-two were confirmed by CCv4 and EndoFLIP as having EGJOO and were clinically managed. Thirteen had MMMD, and nine had IEGJOO. Groups had no difference in demographic data or presenting symptoms by Eckardt score (ES). HRM showed MMMD had greater distal contractile integral, frequency of hypercontractile swallows, and frequency of spastic swallows, and greater DI by EndoFLIP. Patients with MMMD showed greater reduction in symptoms after LES-directed intervention when measured by ES compared with IEGJOO (7.2 vs. 4.0).
Conclusion: Patients with MMMD and IEGJOO present similarly. Detectable differences in HRM portend different responses to endoscopic therapy. Because patients with MMMD have greater short-term prognosis, they should be considered a different diagnostic classification to guide therapy.
Keywords: distal esophageal spasm; endoscopic functional lumen imaging probe; esophageal motility disorders; esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction; high-resolution manometry; hypercontractile esophagus; jackhammer esophagus; lower esophageal sphincter.
© 2023 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
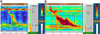

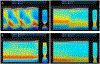
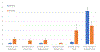
References
-
- Perez-Fernandez MT, Santander C, Marinero A, Burgos-Santamaria D, Chavarria-Herbozo C. Characterization and follow-up of esophagogastric junction outflow obstruction detected by high resolution manometry. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2016;28(1):116–126. - PubMed
-
- Blonski W, Kumar A, Feldman J, Richter JE. Timed Barium Swallow: Diagnostic Role and Predictive Value in Untreated Achalasia, Esophagogastric Junction Outflow Obstruction, and Non-Achalasia Dysphagia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113(2):196–203. - PubMed
-
- Niebisch S, Wilshire CL, Peters JH. Systematic analysis of esophageal pressure topography in high-resolution manometry of 68 normal volunteers. Dis Esophagus. 2013;26(7):651–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

