Delivery of Cervical and Colorectal Cancer Screenings During the Pandemic in Community Health Centers: Practice Changes and Recovery Strategies
- PMID: 37310241
- PMCID: PMC10319245
- DOI: 10.1097/MLR.0000000000001879
Delivery of Cervical and Colorectal Cancer Screenings During the Pandemic in Community Health Centers: Practice Changes and Recovery Strategies
Abstract
Background: The coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic led to clinical practice changes, which affected cancer preventive care delivery.
Objectives: To investigate the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on the delivery of colorectal cancer (CRC) and cervical cancer (CVC) screenings.
Research design: Parallel mixed methods design using electronic health record data (extracted between January 2019 and July 2021). Study results focused on 3 pandemic-related periods: March-May 2020, June-October 2020, and November 2020-September 2021.
Subjects: Two hundred seventeen community health centers located in 13 states and 29 semistructured interviews from 13 community health centers.
Measures: Monthly up-to-date CRC and CVC screening rates and monthly rates of completed colonoscopies, fecal immunochemical test (FIT)/fecal occult blood test (FOBT) procedures, Papanicolaou tests among age and sex-eligible patients. Analysis used generalized estimating equations Poisson modeling. Qualitative analysts developed case summaries and created a cross-case data display for comparison.
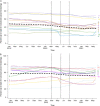
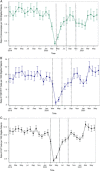
Results: The results showed a reduction of 75% for colonoscopy [rate ratio (RR) = 0.250, 95% CI: 0.224-0.279], 78% for FIT/FOBT (RR = 0.218, 95% CI: 0.208-0.230), and 87% for Papanicolaou (RR = 0.130, 95% CI: 0.125-0.136) rates after the start of the pandemic. During this early pandemic period, CRC screening was impacted by hospitals halting services. Clinic staff moved toward FIT/FOBT screenings. CVC screening was impacted by guidelines encouraging pausing CVC screening, patient reluctance, and concerns about exposure. During the recovery period, leadership-driven preventive care prioritization and quality improvement capacity influenced CRC and CVC screening maintenance and recovery.
Conclusions: Efforts supporting quality improvement capacity could be key actionable elements for these health centers to endure major disruptions to their care delivery system and to drive rapid recovery.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- US Department of Health & Human Services. Notification of Enforcement Discretion for Telehealth Remote Communications During the COVID-19 Nationwide Public Health Emergency. Accessed August 16, 2022. https://www.hhs.gov/hipaa/for-professionals/special-topics/emergency-pre... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

