GeniePool: genomic database with corresponding annotated samples based on a cloud data lake architecture
- PMID: 37311148
- PMCID: PMC10263466
- DOI: 10.1093/database/baad043
GeniePool: genomic database with corresponding annotated samples based on a cloud data lake architecture
Abstract
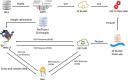
In recent years, there are a huge influx of genomic data and a growing need for its phenotypic correlations, yet existing genomic databases do not allow easy storage and accessibility to the combined phenotypic-genotypic information. Freely accessible allele frequency (AF) databases, such as gnomAD, are crucial for evaluating variants but lack correlated phenotype data. The Sequence Read Archive (SRA) accumulates hundreds of thousands of next-generation sequencing (NGS) samples tagged by their submitters and various attributes. However, samples are stored in large raw format files, inaccessible for a common user. To make thousands of NGS samples and their corresponding additional attributes easily available to clinicians and researchers, we generated a pipeline that continuously downloads raw human NGS data uploaded to SRA using SRAtoolkit and preprocesses them using GATK pipeline. Data are then stored efficiently in a cloud data lake and can be accessed via a representational state transfer application programming interface (REST API) and a user-friendly website. We thus generated GeniePool, a simple and intuitive web service and API for querying NGS data from SRA with direct access to information related to each sample and related studies, providing significant advantages over existing databases for both clinical and research usages. Utilizing data lake infrastructure, we were able to generate a multi-purpose tool that can serve many clinical and research use cases. We expect users to explore the meta-data served via GeniePool both in daily clinical practice and in versatile research endeavours. Database URL https://geniepool.link.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GeniePool 2.0: advancing variant analysis through CHM13-T2T, AlphaMissense, gnomAD V4 integration, and variant co-occurrence queries.Database (Oxford). 2024 Dec 27;2024:baae130. doi: 10.1093/database/baae130. Database (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 39729312 Free PMC article.
-
VCF-Server: A web-based visualization tool for high-throughput variant data mining and management.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Jul;7(7):e00641. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.641. Epub 2019 May 24. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31127704 Free PMC article.
-
NGS-QCbox and Raspberry for Parallel, Automated and Rapid Quality Control Analysis of Large-Scale Next Generation Sequencing (Illumina) Data.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 13;10(10):e0139868. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139868. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26460497 Free PMC article.
-
OTP: An automatized system for managing and processing NGS data.J Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 10;261:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.08.006. Epub 2017 Aug 10. J Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28803971 Review.
-
OpenContami: a web-based application for detecting microbial contaminants in next-generation sequencing data.Bioinformatics. 2021 Sep 29;37(18):3021-3022. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btab101. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 33576798 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GeniePool 2.0: advancing variant analysis through CHM13-T2T, AlphaMissense, gnomAD V4 integration, and variant co-occurrence queries.Database (Oxford). 2024 Dec 27;2024:baae130. doi: 10.1093/database/baae130. Database (Oxford). 2024. PMID: 39729312 Free PMC article.
-
VARista: a free web platform for streamlined whole-genome variant analysis across T2T, hg38, and hg19.Hum Genet. 2024 May;143(5):695-701. doi: 10.1007/s00439-024-02671-4. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38607411
-
Genome-Wide Identification, Evolutionary Expansion, and Expression Analyses of Aux/IAA Gene Family in Castanea mollissima During Seed Kernel Development.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 3;14(7):806. doi: 10.3390/biology14070806. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723365 Free PMC article.
-
Heterozygous THBS2 pathogenic variant causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome with prominent vascular features in humans and mice.Eur J Hum Genet. 2024 May;32(5):550-557. doi: 10.1038/s41431-024-01559-1. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Eur J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38433265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferreira C.R. (2019) The burden of rare diseases. Am. J. Med. Genet. A, 179, 885–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

