A Similarity Renormalization Group Approach to Green's Function Methods
- PMID: 37311565
- PMCID: PMC10339683
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jctc.3c00281
A Similarity Renormalization Group Approach to Green's Function Methods
Abstract
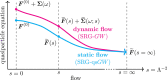
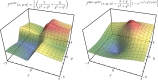
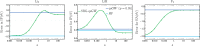
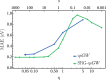
The family of Green's function methods based on the GW approximation has gained popularity in the electronic structure theory thanks to its accuracy in weakly correlated systems combined with its cost-effectiveness. Despite this, self-consistent versions still pose challenges in terms of convergence. A recent study [Monino and Loos J. Chem. Phys. 2022, 156, 231101.] has linked these convergence issues to the intruder-state problem. In this work, a perturbative analysis of the similarity renormalization group (SRG) approach is performed on Green's function methods. The SRG formalism enables us to derive, from first-principles, the expression of a naturally static and Hermitian form of the self-energy that can be employed in quasiparticle self-consistent GW (qsGW) calculations. The resulting SRG-based regularized self-energy significantly accelerates the convergence of qsGW calculations, slightly improves the overall accuracy, and is straightforward to implement in existing code.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Csanak G.; Taylor H.; Yaris R.. Green’s Function Technique in Atomic and Molecular Physics.Advances in atomic and molecular physics; Elsevier: 1971; Vol. 7, pp 287–361.
-
- Fetter A. L.; Waleck J. D.. Quantum Theory of Many Particle Systems; McGraw Hill: San Francisco, 1971.
-
- Martin R. M.; Reining L.; Ceperley D. M.. Interacting Electrons: Theory and Computational Approaches; Cambridge University Press: 2016.
-
- Hedin L. New Method for Calculating the One-Particle Green’s Function with Application to the Electron-Gas Problem. Phys. Rev. 1965, 139, A796.10.1103/PhysRev.139.A796. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

