Development of a Rasch-Built Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Impairment Multidomain Scale to Measure Disease Progression in ALS
- PMID: 37311649
- PMCID: PMC10424842
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207483
Development of a Rasch-Built Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Impairment Multidomain Scale to Measure Disease Progression in ALS
Abstract
Background and objectives: Current scales used in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) attempt to summarize different functional domains or "dimensions" into 1 overall score, which may not accurately characterize the individual patient's disease severity or prognosis. The use of composite score risks declaring treatments ineffective if not all dimensions of ALS disease progression are affected equally. We aimed to develop the ALS Impairment Multidomain Scale (AIMS) to comprehensively characterize disease progression and increase the likelihood of identifying effective treatments.
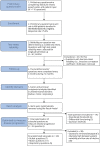
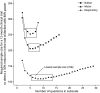
Methods: The Revised ALS Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R) and a preliminary questionnaire, based on literature review and patient input, were completed online by patients from the Netherlands ALS registry at bimonthly intervals over a period of 12 months. A 2-week test-retest, factor analysis, Rasch analysis, and a signal-to-noise optimization strategy were performed to create a multidomain scale. Reliability, longitudinal decline, and associations with survival were evaluated. The sample size required to detect a 35% reduction in progression rate over 6 or 12 months was assessed for a clinical trial that defines the ALSFRS-R or AIMS subscales as a primary endpoint family.
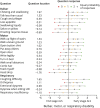
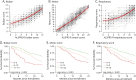
Results: The preliminary questionnaire, consisting of 110 questions, was completed by 367 patients. Three unidimensional subscales were identified, and a multidomain scale was constructed with 7 bulbar, 11 motor, and 5 respiratory questions. Subscales fulfilled Rasch model requirements, with excellent test-retest reliability of 0.91-0.94 and a strong relationship with survival (p < 0.001). Compared with the ALSFRS-R, signal-to-noise ratios were higher as patients declined more uniformly per subscale. Consequently, the estimated sample size reductions achieved with the AIMS compared with those achieved with the ALSFRS-R were 16.3% and 25.9% for 6-month and 12-month clinical trials, respectively.
Discussion: We developed the AIMS, consisting of unidimensional bulbar, motor, and respiratory subscales, which may characterize disease severity better than a total score. AIMS subscales have high test-retest reliability, are optimized to measure disease progression, and are strongly related to survival time. The AIMS can be easily administered and may increase the likelihood of identifying effective treatments in ALS clinical trials.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no relevant disclosures. Go to
Figures

Comment in
-
AIMing for Better Tools to Track Disease Progression.Neurology. 2023 Aug 8;101(6):243-244. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000207500. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Neurology. 2023. PMID: 37311651 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
